Quick Summary
Learn how Drupal DevOps improves development. It uses CI/CD, automated testing, configuration management, and cloud-native practices. This blog explores real-world examples, common problems, and future trends. These include AI-driven testing, decoupled architectures, and shift-left security. Learn how to streamline workflows, enhance performance, and build scalable, secure Drupal sites that are ready for modern demands.
Table of Contents
Many teams struggle with manual deployment, inconsistent environments, and the stress of fixing unexpected bugs in production.
Drupal DevOps combines development and operations into one workflow. This makes deployment easy, automates repetitive tasks, and keeps your site running smoothly every time. With the right tools and practices, you can make Drupal deployments easier. You can set up CI/CD pipelines and use automation. This will help you save time and reduce mistakes.
In this blog, we will show you how to deploy Drupal effectively. We will also discuss the best practices for Drupal DevOps and highlight the benefits. Let’s begin.
What is Drupal DevOps?
Drupal DevOps combines development and operations in a Drupal project. It keeps them running smoothly, stably, and with secure performance. It integrates coding, testing, deployment, and monitoring into a single, consistent workflow. The goal is to reduce delays and speed up the launch.
With Drupal DevOps, teams work in sync instead of handing tasks back and forth. Code goes through automated checks, updates roll out with less risk, and issues surface early before they grow. It also keeps environments consistent, ensuring what works on a developer’s screen works the same in production.
Feel free to hop over to a reddit discussion on Drupal DevOps for further information.
Core Pillars Drupal DevOps
To keep projects steady, predictable, and ready for growth, Drupal DevOps relies on the core pillars outlined below.
CI/CD & Testing
CI/CD pipelines are the backbone of a healthy Drupal workflow. It keeps code moving at a steady pace. Automated tests play a major role here. Drupal supports PHPUnit for backend testing, Kernel tests for deeper logic checks, and Browser tests for full page interactions. Behavior-driven testing also involves validating real user actions rather than just code paths.
A proper CI pipeline runs all these tests. It builds the site, scans for errors, checks coding standards, and flags issues before they ever reach staging. This gives teams the confidence to deploy without fearing regressions. When done right, CI/CD turns deployments into routine steps instead of stressful events.
Configuration Management (CMI)
Drupal’s Configuration Management system helps keep settings consistent across environments. Instead of manual clicks, CMI stores its configuration in files. This includes content types, views, roles, workflows, and many more pieces that shape the site.
With CMI, you export changes from your local environment and import them into staging or production. This prevents configuration drift and stops accidental edits from creeping into live systems. When combined with version control and CI, CMI gives you a clear history of changes and a safe way to roll back mistakes.
Monitoring & Metrics
A Drupal site becomes better with the insights you have behind it. Monitoring tools track performance, memory usage, traffic spikes, slow queries, cache hit ratios, and unexpected errors. Tools like Prometheus and its Drupal integration can provide metrics. These metrics show how the site performs under real load.
These metrics help you catch problems early. A sudden rise in 500 errors can signal problems. A slow database query may also indicate issues. Additionally, a drop in cache efficiency often means trouble is coming. With structured monitoring, you work with facts. It provides you with the awareness needed to keep your Drupal site fast, stable, and predictable.
Infrastructure & DevOps Practices
Infrastructure is the foundation of your Drupal deployment. Modern teams rely on Infrastructure-as-a-Code to define servers, networks, containers, and services using repeatable templates. This eliminates manual setup steps and reduces human error. Tools like Terraform, Ansible, Docker, and Kubernetes enable you to create, modify, and scale environments with precision.
Good DevOps practice means better workflows. This includes peer reviews, automated linting, reliable backups, consistent logging, and secure pipelines. These habits make the entire ecosystem easier to understand and maintain. They also help you scale smoothly when traffic grows or when your team expands.
To use these best practices effectively, hire Drupal developers to build, maintain, and scale your Drupal projects with reliable DevOps workflows.
Benefits of Drupal DevOps
A good DevOps setup can improve how your Drupal projects run. It creates a smooth workflow, reduces delays, and helps teams focus on meaningful work. Below are the key benefits:
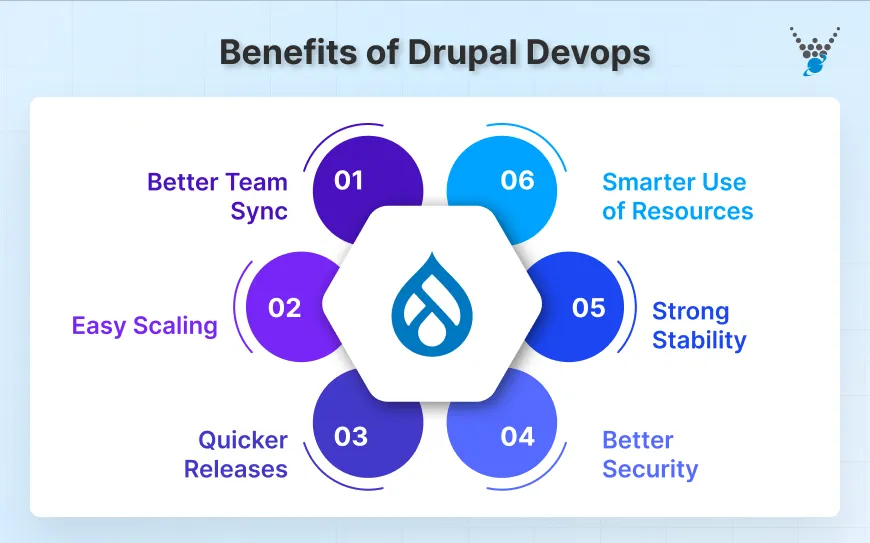
- Better Team Sync: Drupal DevOps brings developers, operations, and QA into a single loop. So the conversations become clearer. The workflow stays consistent, resulting in faster progress and fewer misunderstandings.
- Quicker Releases: With automated builds and clean deployment pipelines, new features reach production faster. You spend less time fixing mistakes and more time on improving things that users actually notice.
- Stronger Stability: Automated tests and continuous monitoring are DevOps practices that catch problems before they grow. They lead to a more stable Drupal site where updates are safe, and outages are rare.
- Easy Scaling: As traffic increases, Drupal DevOps helps you scale with minimal stress. Cloud-based tools and scripted environments let you add resources on demand and maintain smooth performance during peak loads.
- Smarter Use of Resources: Routine tasks are automated, so teams don’t have to do repetitive work. You use cloud infrastructure with precision, helping you cut waste and keep your system lean.
- Better Security: Security checks run in the background, scanning for weak spots and unusual behavior. This constant vigilance keeps your Drupal site protected and reduces the risk of costly breaches.
Put simply, Drupal DevOps makes work easier and faster. It brings teams together, automates tasks, and cuts down on delays. It strengthens stability, improves security, supports easy scaling, and enables quicker releases with far less stress.
Common Challenges of Drupal DevOps
Adopting DevOps for Drupal offers many benefits, but there are a few challenges that you need to deal with. Below are some of them:
Environment Inconsistencies
Drupal is sensitive to even small differences in PHP versions, extensions, server settings, or cache layers. When your local setup doesn’t mirror staging or production, bugs can appear that you cannot reproduce.
Dependency Management Issues
A Drupal site depends on core files, contributed modules, libraries, Composer packages, and sometimes custom patches. If one environment pulls an outdated package or a missing patch, the entire site behaves unpredictably. This is not a minor nuisance. Poor dependency files can take down a release.
Configuration Changes
Drupal stores configuration across files and the database. When someone makes a quick fix directly on production or forgets to export changes, they change your environments. Over time, it becomes a silent threat that eventually causes issues with features during deployment.
End-to-End Testing Gaps
Testing a Drupal project involves more than just checking page loads. Permissions, content workflows, caching behavior, and module interactions all require thorough testing. Many teams avoid full-path testing because it takes a lot of time. However, skipping it can cause problems later that are much more expensive to fix.
Security Risks During Deployment
Drupal deployments involve updates, database changes, and new modules, each with risks. Rushing with incorrect permissions or unchecked modules can create security issues. Deployment security should be treated as a skill, not just a checklist.
Scaling Challenges
Scaling a Drupal site seems easy until there is a traffic surge. A campaign, a product launch, or a seasonal spike can slow down the server within minutes. To keep the site responsive, you should spread the load across multiple servers. You also need to adjust caching layers, improve the database, and set up load balancers.
In self-managed setups, this process can be tricky and prone to errors. Each new server or container needs careful configuration. One missed setting can leave a slow node in the cluster and bring performance down for everyone.
Lack of Attention to Actual User Needs
DevOps teams often obsess over pipelines and automation, forgetting the people using the site. When teams focus on optimization instead of outcomes, they create technically good deployments. However, these do not solve real user problems.
This disconnect slows meaningful progress.
Weak Standards and Metrics
Without clear benchmarks such as deployment time, rollback time, test coverage, and performance targets, teams operate blindly. In Drupal’s layered architecture, weak metrics hide the true causes of issues, making improvement difficult.
Resistance to Change
Drupal teams often have set workflows. Introducing DevOps brings new tools, shared responsibility, and tighter feedback loops. Some members resist because DevOps exposes inefficiencies and demands accountability. This cultural shift is often more challenging than the technical work.
Integrating Tools Across Domains
Drupal DevOps relies on a series of tools. These include CI servers, testing suites, deployment pipelines, monitoring systems, and cloud services. All these tools must work together. The challenge is getting each tool to communicate cleanly so builds, tests, and deployments run without friction.
Even minor differences between systems can break the flow, stall releases, or create blind spots in production. Keeping this entire toolchain synchronized ranks as one of the most demanding parts of running Drupal at scale.
In short, Drupal DevOps has challenges. These include inconsistent environments, weak dependencies, scaling issues, and gaps in testing or security. Many teams struggle with tool integration, weak standards, and cultural resistance. This makes smooth and predictable delivery harder than it seems.
If you are having trouble with these Drupal DevOps challenges, think about working with a trusted Drupal development company to ensure reliable deployments.
Real-World Use Cases of Drupal DevOps
To explain DevOps in a clearer way, Drupal has many examples. These show how a good workflow can save failing projects.
BCT Partners
BCT Partners experienced a critical breakdown in their deployment workflow, halting progress. It put a significant project at risk. Their environments were unstable, releases kept failing, and the team struggled to diagnose the root cause.
They rebuilt their DevOps pipeline with clear automation, consistent environments, and clean deployment rules. This restored reliability within a single demo session. The change brought discipline back into the workflow and turned a fragile setup into a steady, predictable system.
GitLab Auto
GitLab Auto showed how far automation can take a Drupal project. With Drupal DevOps, projects benefit from automated builds, tests, containerization, security scans, and deployments without manual wiring. The pipeline detects the project’s structure, prepares the environment, and executes each step with accuracy.
For teams that follow DevOps practices without building every tool by hand, Auto DevOps offers a clear path that is fast, repeatable, and aligned with modern Drupal engineering practices.
Future Trends in Drupal DevOps
Drupal DevOps is moving into a far more dynamic space. Modern architecture and smarter tooling shape it. Below are some trends that are gaining pace.
Decoupled and Headless Drupal
More teams are adopting decoupled or headless architectures. In this, Drupal handles the backend, while modern frontends such as React or Vue.js manage the user interface. This separation creates better experiences and allows for quicker updates. For DevOps, it means managing two codebases, syncing deployments, and ensuring the backend and frontend work together.
Cloud-Native Technologies
Cloud-native platforms are increasingly being used for Drupal deployments. Containerization with Docker, orchestration with Kubernetes, and serverless functions offer scalability, resilience, and flexibility. DevOps teams must manage containers, automate scaling, and monitor distributed environments to ensure consistent performance across all nodes.
AI and Automation in Testing
Automated testing remains essential, but AI now guides test coverage. Predictive testing identifies code areas prone to failure, optimizes test runs, and improves efficiency. Using traditional PHPUnit, Kernel, and Browser tests along with AI-driven testing helps teams find problems early. This approach does not slow down development.
Infrastructure as Code
Infrastructure as Code is becoming standard practice in Drupal DevOps. Using tools like Terraform and Ansible, teams define servers, networks, and services as code. This ensures environments are consistent, repeatable, and easy to scale. It reduces human error and streamlines deployment.
Enhanced CI/CD Pipelines
Modern pipelines now include security checks, performance tests, and advanced deployment strategies like canary releases and rollbacks. These improvements deploy faster, safer, and more predictably.
Monitoring and Real-Time Analytics
Advanced monitoring tools provide insights into performance, traffic, errors, and caching efficiency. Real-time analytics help teams identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and maintain reliability. Integrating these tools into DevOps workflows ensures proactive maintenance instead of reactive troubleshooting.
Shift-Left Security
Security is shifting earlier in the development lifecycle. Developers integrate static code analysis, vulnerability scanning, and compliance checks directly into pipelines. This proactive approach reduces risks and ensures Drupal sites are secure from the start.
Blockchain and Decentralization
While still experimental, blockchain can enable secure, tamper-proof transactions and trusted data management. Certain Drupal applications could use it for high-security environments, adding a new layer to future DevOps considerations.
Drupal DevOps is evolving with decoupled architectures, cloud-native platforms, AI-driven testing, and Infrastructure-as-Code, making workflows faster, more innovative, and more reliable. Enhanced CI/CD, real-time monitoring, shift-left security, and emerging technologies like blockchain will make Drupal deployments more scalable and secure.
Conclusion
Drupal DevOps is like a mindset that changes how teams build, deploy, and maintain websites. By combining CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, configuration management, and monitoring, teams can deliver Drupal projects faster, more reliably, and more securely. Modern practices like cloud-native deployments, AI-driven testing, and Infrastructure-as-Code make workflows easier and more reliable. They help reduce errors and downtime.
The case study of BCT Partners and GitLab Auto DevOps shows how structured pipelines and automation can save fragile deployments and streamline complex workflows. Upcoming trends like decoupled architectures, shift-left security, and advanced analytics show where Drupal DevOps is heading. These trends ensure scalability, performance, and adaptability for modern web experiences.
If you’re planning to implement Drupal DevOps practices or optimize your current workflows, our team can help. Contact us today to streamline your deployments, enhance stability, and make your Drupal projects more efficient.
FAQs on Drupal DevOps
Why is DevOps important for Drupal projects?
DevOps brings structure and speed to Drupal development. It ensures code moves reliably from development to production, reduces errors, and allows teams to deploy updates faster. By combining automation, monitoring, and collaboration, DevOps helps maintain stability, improves site performance, and makes complex Drupal workflows predictable and manageable.
Which tools does Drupal DevOps use?
Drupal DevOps relies on a mix of tools for automation, monitoring, and infrastructure. Common ones include CI/CD tools like GitLab CI and Jenkins, testing frameworks like PHPUnit and Behat, container tools like Docker and Kubernetes, infrastructure tools such as Terraform and Ansible, and monitoring platforms like Prometheus. Together, they streamline development and deployment workflows.
How does CI/CD work in Drupal?
CI/CD automates the build, testing, and deployment of Drupal projects. Every code change triggers automated tests, scans, and environment builds. If tests pass, updates are deployed to staging or production. This process reduces manual errors, ensures consistent quality, and allows teams to release features more frequently without risking downtime.
What is Drupal Configuration Management (CMI)?
Drupal’s Configuration Management system stores site settings, like content types, views, workflows, and roles, in files. These files can be exported, versioned, and imported across environments. CMI prevents configuration drift, keeps environments consistent, and allows safe rollbacks, making deployment and collaboration much easier.
How do containers (Docker/Kubernetes) help Drupal DevOps?
Containers package Drupal with all its dependencies, ensuring it runs the same everywhere from local development to production. Kubernetes and orchestration tools manage scaling, load distribution, and failover automatically. This approach reduces setup errors, simplifies updates, and makes it easier to handle traffic spikes efficiently.
Talk to Our Experts
Need support? Talk to a DevOps expert for smarter, efficient, and automated Drupal deployments.





