Quick Summary
Looking to scale your web apps efficiently? This guide explores how Laravel’s robust features pair perfectly with microservices architecture, enabling modular, independent, and highly scalable services. Discover step-by-step implementation, communication strategies, best practices, and solutions to challenges like deployment complexity, debugging, and data consistency. This lets developers build resilient, agile, and maintainable large-scale applications.
Table of Contents
Building reliable and flexible systems has become a priority as applications grow in size and traffic. Many teams start with a single codebase, but over time, this approach can slow development and create scaling issues. That’s where Laravel Microservices come into play. They offer a way to break a large project into smaller, independent services that work together. Each service handles one job and does it well, making the entire system easier to manage and scale.
Laravel provides a clean structure, expressive syntax, and strong tooling that help developers build and maintain services without unnecessary complexity. This approach supports long-term growth, reduces deployment risks, and allows teams to work in parallel with less interference.
In this guide, we’ll discuss how microservices fit within modern development needs, the practical steps to implement them in Laravel, and the best practices that keep everything stable and secure. Let’s begin.
What are Laravel Microservices?
Laravel microservices refer to building your application as a group of small, separate services instead of one large codebase. Each service handles one focused task. For example, one service may manage user accounts, another may manage payments, and another may handle notifications. These services communicate through APIs and work together as a complete system.
This approach is different from the traditional “all-in-one” application structure. In a single large system, one change can affect many parts of the application. It can slow development and make debugging more tiring. In microservices, each service runs independently. You can update, scale, or even replace a single service without affecting the others.
You can think of it like organizing a team where everyone has one clear job, instead of one person trying to do everything.
It usually leads to:
- Simpler troubleshooting, since issues are isolated
- Faster development, because services can be worked on in parallel
- Easier scaling, as you only scale what needs more power
Laravel makes this structure approachable because of its clean coding style, API tools, and support for queues and communication layers. Laravel microservices architecture uses these strengths to keep each service neat, predictable, and easy to maintain over time.
Benefits of Using Microservices in Laravel
Using microservices in Laravel brings clarity, speed, and control to your application. Instead of handling one huge codebase, you work with small, focused services. Each service has a single responsibility, making it easier to develop, test, and maintain.
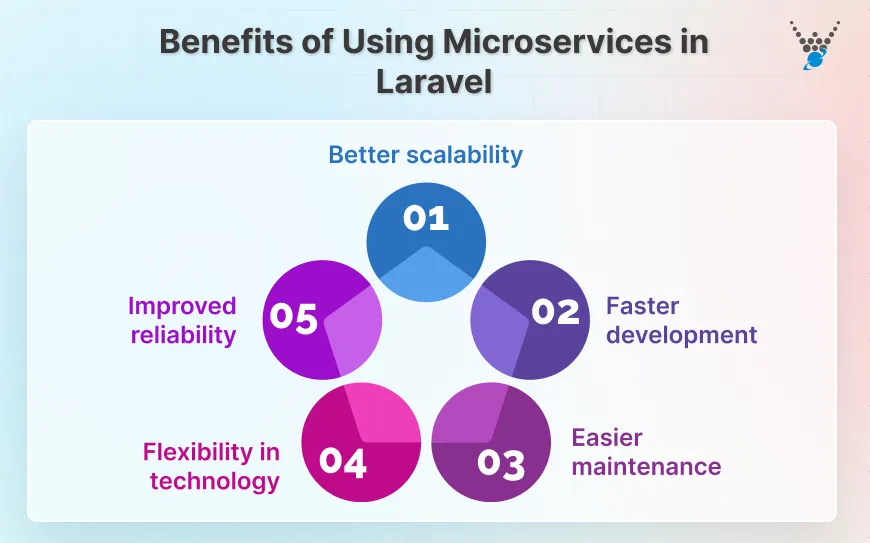
Some key benefits include:
- Better scalability: You can scale only the parts of your application that need more resources, without touching everything else.
- Faster development: Teams can work on multiple services simultaneously, reducing bottlenecks and speeding up delivery.
- Easier maintenance: When something breaks, it’s isolated to a single service. Debugging becomes simpler and less risky.
- Flexibility in technology: You can choose different tools or languages for specific services if needed, without rewriting the whole system.
- Improved reliability: If one service fails, it doesn’t necessarily take down the entire application.
Laravel’s elegant structure and rich ecosystem make it a strong choice for this approach. It’s especially valuable when building large-scale Laravel applications, where growth and complexity can otherwise slow teams down or introduce errors.
How can Laravel be Used with Microservices?
Laravel provides several features and tools that make it well-suited for developing microservices-based applications. Here are some key ways to use Laravel with microservices:
- Service Segmentation: Utilize Laravel to break down the application into smaller, manageable services, each responsible for specific business functions. For example, user management, order processing, and inventory management can be separate services.
- API Development: Use Laravel to develop RESTful APIs for each microservice, allowing them to communicate and interact with each other seamlessly.
- Containerization: Implement Docker to containerize each microservice, ensuring they are isolated, portable, and can run consistently across different environments.
- Scaling and Load Balancing: Utilize Laravel Horizon and Supervisor for managing queues and background processes, enabling efficient scaling and load balancing of microservices.
- Event-Driven Architecture: Take advantage of Laravel’s event broadcasting and listening capabilities to establish a reliable event-driven communication system between microservices.
Laravel’s emphasis on modularity and separation of concerns enables the development and maintenance of independent microservices with ease. This approach is especially beneficial for large-scale applications. Optimizing route structures across services becomes more efficient when applying advanced routing techniques in Laravel, ensuring better organization and scalability.
Steps for Creating a Microservice with Laravel
Creating a microservice with Laravel can help make the development process of larger sites and apps much more streamlined. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps:
Step 1: Create a new Laravel web project using the composer create-project command.
Step 2: Design the database schema and create the necessary migrations using the artisan command-line tool.
Step 3: Develop the microservice functionality by creating controllers, models, and routes using Laravel’s built-in features.
Step 4: Implement authentication and authorization logic to secure the microservice endpoints. To gain finer control over access management, see how Laravel policies and gates enhance your authorization strategy.
Step 5: Use the Laravel Queue System to manage asynchronous tasks and handle background jobs efficiently. It helps improve application performance by processing time-consuming operations in the background, ensuring smoother and faster user experiences.
When creating a microservice with Laravel, make sure you use the Laravel Passport for API authentication. Also, consider using Vue.js to build interactive single-page applications that can consume the microservice APIs.
If you need help with this technical process, consult with a Laravel development company. They can help create the best microservices depending on the required capabilities.
How does Laravel Handle Communication Between Microservices?
Laravel offers several ways to handle communications between microservices, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
HTTP/REST APIs
This is the most common approach for microservice communication. Laravel provides built-in features like routing and controllers to develop and expose RESTful APIs for your microservices easily.
- Advantages: Simple to implement, familiar to most developers, supports various HTTP verbs and data formats.
- Disadvantages: It can be inefficient for complex interactions, has limited fault tolerance, and requires careful security considerations.
Queues
Laravel’s built-in queue system can be used to send asynchronous messages between microservices. This is useful for tasks that don’t require immediate responses or for decoupling services that don’t need to be directly connected.
- Advantages: Decouples services, improves scalability and fault tolerance, handles long-running tasks efficiently.
- Disadvantages: Adds complexity and requires additional infrastructure like message brokers (e.g., RabbitMQ, Kafka).
Messaging Protocols
Laravel can be integrated with various messaging protocols like AMQP (RabbitMQ) or MQTT for more complex communication scenarios. These protocols offer features like guaranteed delivery, message queuing, and publish-subscribe patterns.
- Advantages: High reliability and scalability, supports complex communication patterns, suitable for distributed systems.
- Disadvantages: Requires additional configuration and setup, steeper learning curve compared to HTTP APIs.
Service Discovery and Orchestration
Tools like Consul or Zookeeper can help with service discovery, allowing microservices to locate and communicate with each other dynamically.
- Advantages: Dynamically manage service availability, simplifies communication and integration between services.
- Disadvantages: It adds another layer of complexity and requires additional infrastructure and configuration.
Laravel Packages
Several Laravel packages specifically address microservice communication challenges, such as Laravel Horizon (queue management), Laravel Envoy (deployment automation), and Laravel Telescope (distributed tracing and monitoring).
- Advantages: Can simplify specific tasks and automate processes, often integrating seamlessly with the Laravel framework.
- Disadvantages: It may introduce additional dependencies that require learning new APIs and functionalities.
The ideal communication method between microservices depends on factors such as message complexity, performance requirements, fault tolerance, and scalability. Choosing the right strategy ensures seamless interaction within your Laravel microservices architecture. To enable real-time capabilities, webSockets in Laravel offer an effective way to build event-driven and responsive applications.
Best Practices for Using Laravel with Microservices
When working with microservices in Laravel, the goal is to keep your system simple to scale, easy to maintain, and stable as it grows. The following best practices help ensure that your Laravel API microservices stay clean and dependable:
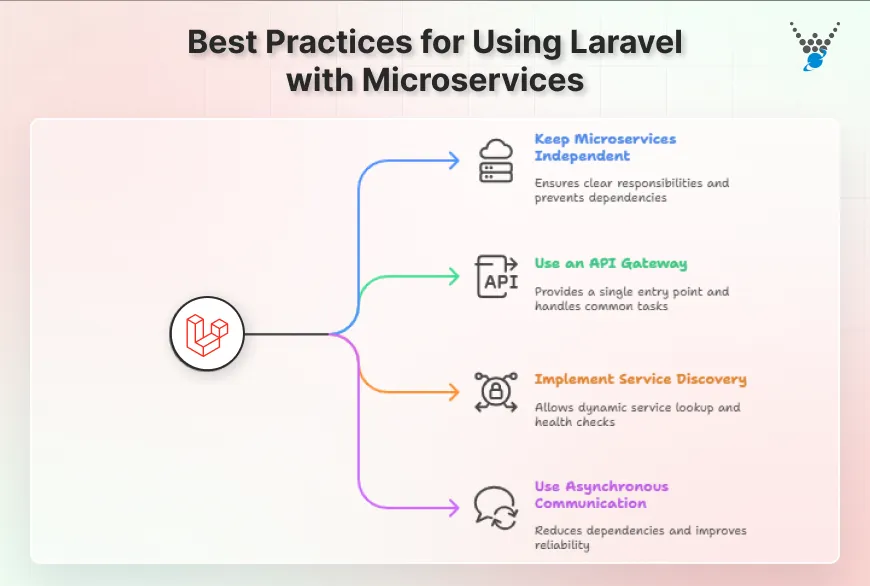
Keep Each Microservice Independent
- Give each service one clear responsibility.
- Define strict boundaries so services don’t overlap or depend too heavily on each other.
- Let services communicate through well-defined APIs.
- Use separate databases to prevent shared data issues.
- Use container tools like Docker and orchestration tools like Kubernetes to manage services individually.
Use an API Gateway
- Provide a single entry point for all client requests.
- Handle authentication, rate limiting, logging, and routing at the gateway level.
- Keep clients unaware of internal service complexity.
- Use the gateway to support versioning so updates don’t break existing clients.
Implement Service Discovery
- Register each service automatically when it runs, using tools such as Consul or built-in registry components.
- Let services look up others dynamically instead of hardcoding locations.
- Add regular health checks to ensure only active and healthy services are used.
Use Asynchronous Communication Where Possible
- Use queues or message brokers like RabbitMQ or Kafka for background tasks.
- Let services communicate through events, reducing direct dependencies.
- Add proper error handling and retry logic to prevent message loss.
Simply put, keep your Laravel API microservices small, independent, and connected via clear APIs, each with its own data and deployment environments. Use API gateways, service discovery, and asynchronous communication to simplify routing, improve reliability, and support smooth scaling as the system grows.
Challenges of Using Laravel with Microservices
Working with microservices in Laravel can introduce new complexity. Here are the main challenges and how to manage them effectively:
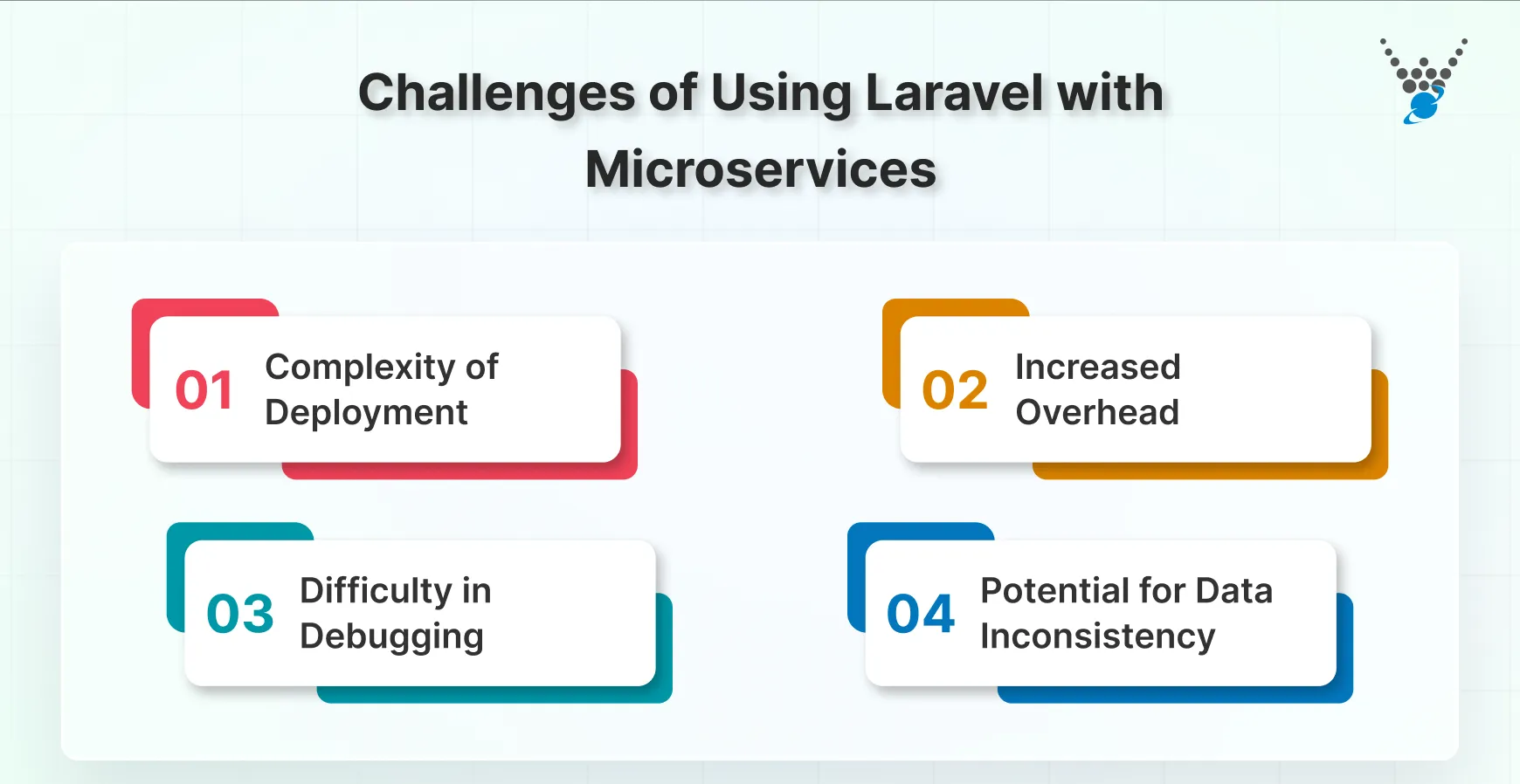
Complexity of Deployment
Deploying many small services can feel overwhelming. Automation helps keep things consistent and repeatable. Use Docker to package each service cleanly. Define your infrastructure using tools like Terraform or CloudFormation so every environment matches.
A CI/CD pipeline ensures each service is built, tested, and deployed smoothly. Keep deployment steps documented and make sure the team understands the workflow.
Increased Overhead
Microservices introduce more network communication and system coordination. This can demand extra resources. Optimize service-to-service communication and use load balancing to handle traffic effectively. Automate monitoring and deployment so the team isn’t weighed down with manual management.
Difficulty in Debugging
Debugging becomes more difficult because a single request may traverse many services. Logging is essential to trace what happened and where. Use tools like Sentry or New Relic to quickly catch errors. Add distributed tracing with Jaeger or Zipkin to trace a request across services. Centralized error handling keeps behavior consistent and easier to understand.
Potential for Data Inconsistency
Different services may hold different versions of the data at any given time. To handle this, use patterns like event sourcing or distributed transactions when strong consistency is required. For operations that may be retried, use idempotent actions to avoid duplicates.
Allow eventual consistency when real-time accuracy isn’t critical. Periodically reconcile data to ensure everything stays aligned.With these implementations, you can effectively prevent data inconsistencies. Or you can hire Laravel developer who has the expertise to ensure these challenges never arise.
| What Our Experts Say |
|---|
| “Decide your communication pattern before building any services. Whether you choose API calls or an event-driven approach, stick to one primary method. Most issues in Laravel microservices architecture come from mixing patterns without a plan. Define message formats, error responses, and versioning rules early. This prevents hidden dependencies and saves you from major rewrites later.“ |
Conclusion
While Laravel can help create some outstanding sites and web apps, microservices are an architectural approach for ensuring modularity and scalability. It also allows for better code organization and separation of concerns, making it easier to manage and update specific parts of the application.
You can use microservices with Laravel to create everything from small sites to massive eCommerce outlets, content management systems, and social platforms.
If you want more info or support for implementing Laravel and microservices, have a talk with our experts today!
FAQs on Laravel and Microservices
Do I need to have prior knowledge of Laravel or Microservices to use this guide?
While having some familiarity with Laravel or microservices can be helpful, this comprehensive guide is designed to be beginner-friendly and does not require prior knowledge of either. It provides a step-by-step approach and thorough explanations to help beginners understand and implement these concepts.
Can I use Laravel and Microservices for any type of web application?
Yes, Laravel and microservices can be used for various types of web applications, including e-commerce sites, content management systems, and social media platforms. The flexibility and scalability of this combination make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Are there any downsides to using Laravel and Microservices?
While the benefits of using Laravel and microservices are significant, there are some potential downsides to consider. This approach can lead to a more complex system, which may require additional resources and expertise. It also requires careful planning and design to ensure proper communication and coordination between microservices.
Build Powerful Laravel Applications
Learn how to leverage Laravel's powerful features for efficient and scalable web development.





