Quick Summary
Laravel and React are two very powerful tools for web development, each serving different needs. Laravel is a PHP framework that makes backend development secure, fast, and organized. React is a JavaScript library that builds dynamic, responsive, and user-friendly interfaces. This blog compares their features, pros and cons, use cases, and shows how they can even work together to build scalable, modern web apps.
Table of Contents
Developers use a range of web development tools to build websites and applications efficiently. They streamline the processes and ensure high-quality results. From robust frameworks to versatile libraries, the right development tool can significantly impact your project’s success.
But with a vast array of options available, choosing the perfect one can be a challenge. However, two of the most popular choices are Laravel and React.
In this blog, we will compare Laravel and React based on a few key factors, so you can make an informed decision. Plus, I will give you an idea on when the web experts use these two technologies. Let’s begin.
What is Laravel?
Laravel is a robust, open-source PHP web framework designed for building modern web applications. It follows a well-organized MVC structure, keeping code clean and easy to manage. This, along with its clear syntax, makes development simple and fast.
One of Laravel’s key advantages is its robust routing system and caching, which enhance development productivity. Laravel also offers tools for task scheduling, queue systems for background jobs, and unit testing. Plus, its regular updates and resources ensure that developers follow the best Laravel security practices.
Key Features of Laravel
Laravel simplifies web development with several features that ensure the application is robust, secure, and maintainable. Here’s a closer look at some of its key features:
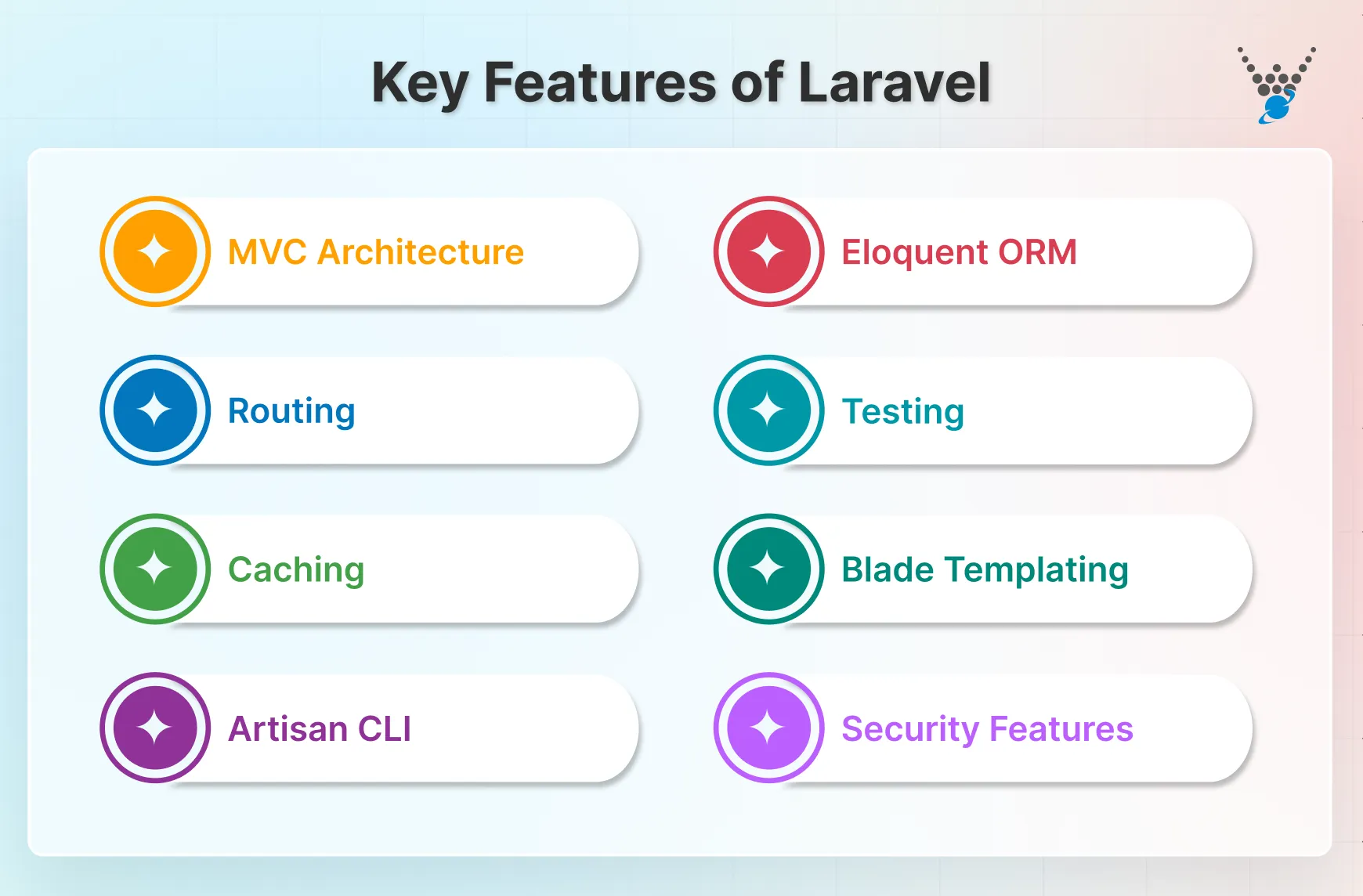
- MVC Architecture: Laravel ensures a clear separation of concerns using the MVC pattern. This promotes clean, maintainable code by dividing the application into Models, Views, and Controllers.
- Eloquent ORM is a powerful Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) that simplifies database interactions. Using Eloquent techniques, you can interact with databases using PHP syntax instead of writing raw SQL queries.
- Routing: Laravel offers a flexible routing system that allows you to define routes for both RESTful and non-RESTful web apps. The routing system supports route grouping, middleware, and resource controllers. That simplifies managing and organizing application routes.
- Testing: Laravel provides robust support for unit testing with PHPUnit. You can write and run tests easily, ensuring that the application functions as expected and reducing the chances of bugs.
- Caching: The Laravel caching mechanism lets you store frequently accessed data in memory, reducing database load times. This increases application performance, reducing the response time for users.
- Blade Templating: The Laravel Blade templating offers a powerful yet lightweight way to structure your application’s views. Blade syntax integrates seamlessly with PHP code, so you can write logic and manipulate data within templates.
- Artisan CLI: Laravel’s Artisan command-line interface (CLI) automates repetitive tasks like generating code and Laravel database migrations. It helps developers keep their database schema in sync and manage seeding databases in Laravel for testing purposes.
- Security Features: Laravel prioritizes security with built-in features like input validation, preventing malicious attacks like SQL injection. Plus, password hashing ensures secure storage of user credentials, and CSRF protection safeguards against unauthorized actions.
Pros and Cons of Laravel
Let’s look at some of the pros and cons of Laravel through a quick table.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to learn. Laravel has a simple syntax that beginners can pick up quickly. | Learning curve for advanced features. Some tools take extra time to understand. |
| Built-in tools. Things like authentication, routing, and caching are already included. | Heavier framework. Compared to smaller frameworks, it can feel bulky. |
| Strong community support. Many tutorials, forums, and packages are available. | Hosting limitations. Not every budget hosting plan supports Laravel well. |
| Scalable. Works well for small apps and can grow into larger systems. | Performance trade-offs. It is not always the fastest choice if speed is the only focus. |
| MVC structure. Keeps code organized and makes projects easier to maintain. | Frequent updates. Some teams may struggle to keep up with changes. |
Simply put, Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that makes building modern web applications faster, cleaner, and more secure with features like MVC architecture, Eloquent ORM, and Blade templating. It offers built-in tools, strong community support, and scalability, though advanced features and hosting needs can add complexity.So, if you want to build a secure, scalable, and high-performing web app, opt for our Laravel development services.
What is React?
React is an open-source JavaScript library created by Meta for building user interfaces (UIs) of web applications. It lets you build complex UIs from smaller, reusable pieces called components. Using its state management system, you can manage components and handle dynamic data.
One of React’s key features is its virtual DOM. It allows rendering specific elements on the web page without reloading the entire page. This client-side rendering enhances the performance of web apps, making them more responsive and user-friendly. It is especially useful for applications where real-time data updates are crucial.
Key Features of React
React offers a range of features, from virtual DOM to hooks, making it a powerful library for building user interfaces. Here are some of the key features that make React in detail:
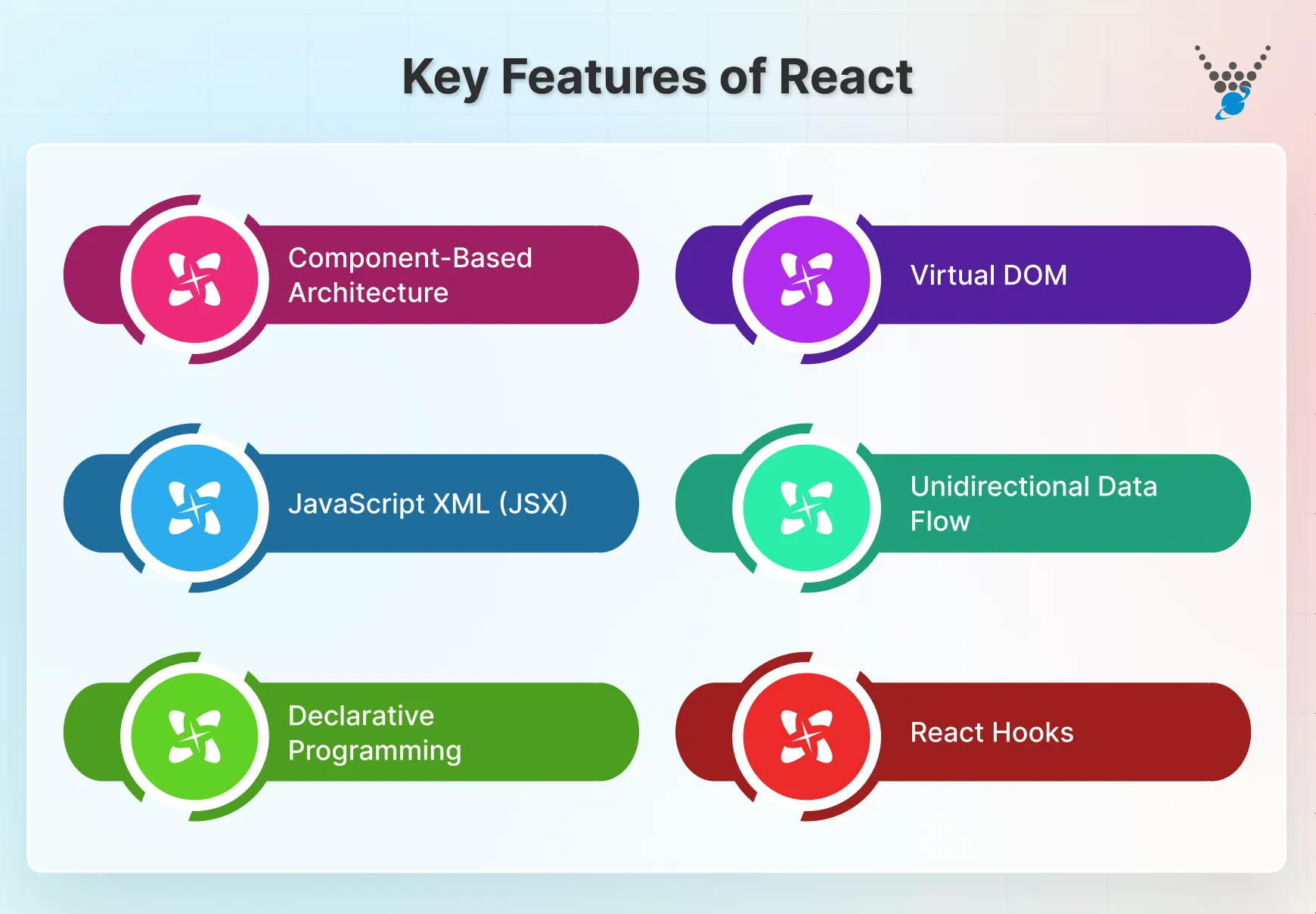
- Component-Based Architecture: React applications are built by composing independent, reusable components of code. These components contain logic and UI functionality; this modularity promotes code reuse and easier maintenance.
- Virtual DOM: React uses a virtual DOM, a lightweight representation of the browser’s Document Object Model (DOM). When changes occur in the application, React compares the virtual DOM with the previous version and updates the least changes required in the real DOM. This ensures faster and efficient updates.
- JSX: JavaScript XML (JSX) is a syntax extension for JavaScript that allows you to write HTML-like code within JavaScript. JSX makes it easier to visualize the structure of the UI helping you write cleaner and more readable code.
- Unidirectional Data Flow: React has a unidirectional data flow. Data is passed down from parent components to child components through properties. This flow makes it easier to know how data changes affect the UI, leading to more maintainable applications.
- Declarative Programming: You can describe the desired state of your UI using components and props. This approach simplifies development by focusing on what the UI should look like rather than how it should be manipulated.
- React Hooks: It provides a powerful way to manage state and side effects within functional components. Hooks allow you to reuse stateful logic without defining class-based components. This makes functional components more versatile and easier to use.
Pros and Cons of React
Here is a quick comparison of React’s pros and cons.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to use. The component-based approach makes code reusable and easy to manage. | React updates often. This makes it hard to keep up with. |
| Strong community. Massive support from developers and plenty of learning resources. | Steeper learning curve for beginners. JSX and concepts like state may feel confusing at first. |
| High performance. Virtual DOM makes apps run smoothly and respond quickly. | Needs extra tools. For routing or state management, you need other libraries. |
| Flexible. It can be used for both small projects and large-scale apps. | Too many choices. The ecosystem is vast and can overwhelm new developers. |
| Backed by Meta. Constant improvements and long-term support give it reliability. | Not SEO friendly out of the box. Server-side rendering is needed for better SEO. |
In short, React is a popular JavaScript library by Meta that helps build fast, dynamic, and reusable user interfaces using components and a virtual DOM. It delivers high performance and flexibility, though beginners may face a learning curve and often need extra tools for advanced features.If you want to create a powerful, interactive web application, hire React JS developers to build scalable, high-performing solutions tailored to your business needs.
Laravel vs React: Comparison Table
Laravel and React are tools for making web development efficient, yet they differ in most aspects. Here’s a comparison table to help you understand the key differences between Laravel and React:
| Feature | Laravel | React |
|---|---|---|
| Type | PHP Framework | JavaScript Library |
| Architecture | MVC (Model-View-Controller) | Component-Based |
| Primary Use | Backend Development | Frontend Development |
| Templating Engine | Blade | JSX |
| State Management | Built-in (via MVC) | Hooks, Context API, Third-party (e.g., Redux) |
| Routing | Built-in | React Router |
| Data Handling | Eloquent ORM for Database Management | Fetch APIs, GraphQL, etc. |
| Performance Optimization | Caching, Queues, Task Scheduling | Virtual DOM, Memoization, Lazy Loading |
| Testing | PHPUnit, Built-in Testing Tools | Jest, Enzyme, React Testing Library |
| Command-line Interface | Artisan CLI | Create React App CLI |
| Server-Side Rendering (SSR) | Supported via Laravel Echo and Packages | Supported via Next.js |
| Security | Built-in (CSRF, XSS, Encryption) | Depends on implementation, often via third-party tools |
| Community and Ecosystem | Large Community, Rich Ecosystem, Composer Packages | Large Community, Rich Ecosystem, npm/yarn Packages |
| Real-Time Support | Pusher, Laravel Echo | WebSockets, Third-party Libraries |
| Flexibility | Best suited for complex backend applications | Best suited for dynamic and interactive UIs |
Comprehensive Difference Between Laravel and React
While Laravel and React are popular tools in web development, they serve vastly different purposes. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of their key differences to help you choose the right one for your project:
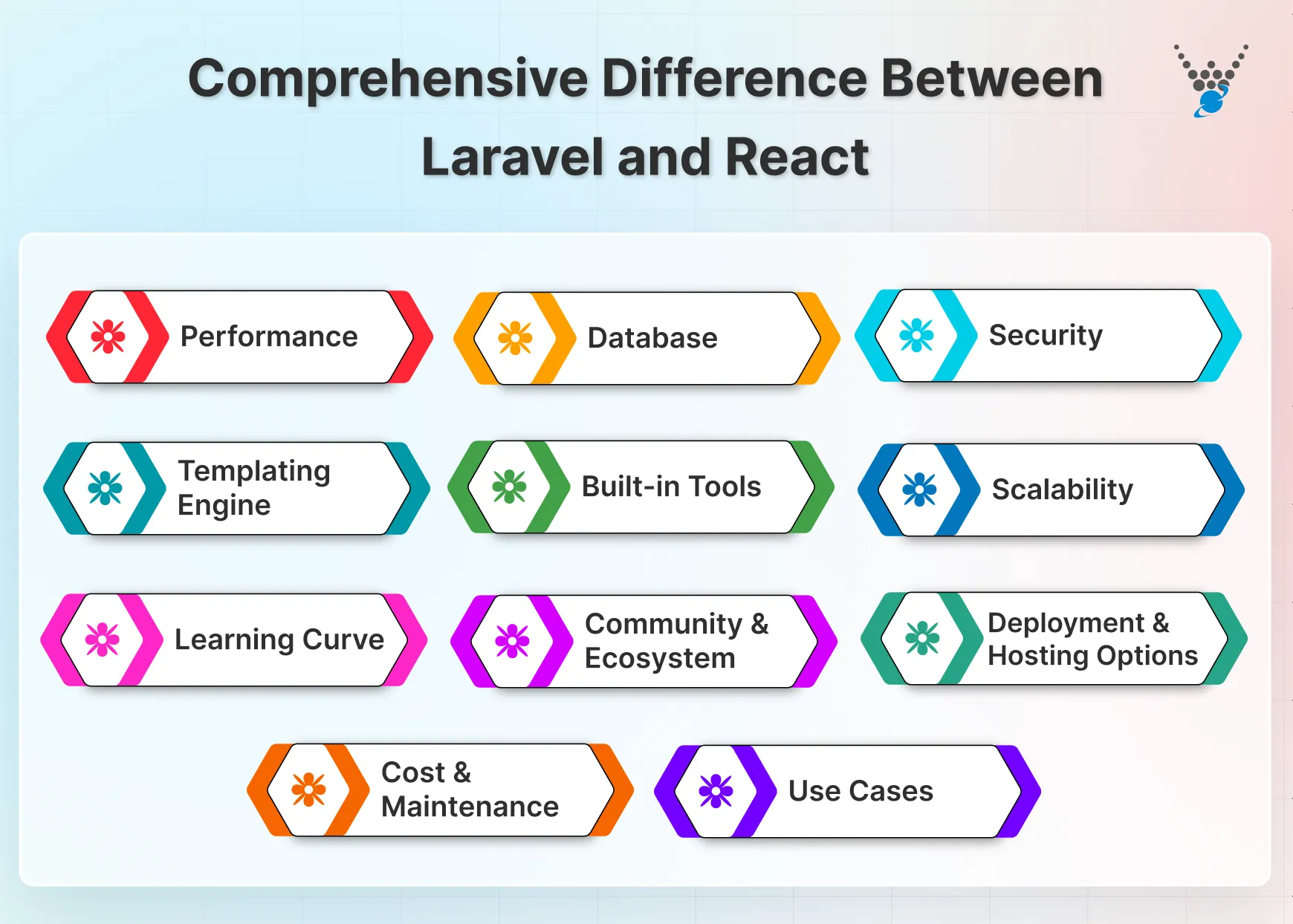
Performance
Laravel follows the MVC architecture, where web pages are rendered entirely on the server. This can be slightly slower for dynamic applications with frequent content updates. However, by caching frequently accessed data and views, Laravel can significantly improve application performance.
React, on the other hand, uses a virtual DOM and component-based architecture. It focuses on client-side rendering, sending only necessary UI updates to the browser. This makes React applications fast and responsive, especially for applications with much user interaction. It results in a smooth user experience.
Verdict
When it comes to responsiveness and user experience, React takes the clear lead. However, for heavy websites where initial page load time is crucial, Laravel’s caching capabilities can be highly effective.
Database
Laravel comes with Eloquent ORM, which provides an intuitive and simple way to interact with databases. Eloquent simplifies complex database queries and relationships, making it easy to manage data. Laravel supports multiple database systems, offers migration and seeding tools to manage schema changes effectively.
React is a frontend library that does not handle database interactions directly. Instead, it relies on APIs like RESTful APIs to communicate with the backend database. This makes React flexible, as it can work with any backend technology that can provide data via APIs.
Verdict
Laravel provides built-in database management capabilities with Eloquent ORM, making it a good choice for database interactions. React, being a frontend library, relies on backend APIs for data management.
Security
Laravel includes built-in security features to protect against vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). It uses hashed passwords with the Bcrypt hashing algorithm, which provides an easy way to handle user authentication and authorization.
As a UI library, React doesn’t have built-in security features. Security in React applications depends on how well developers leverage external tools and libraries. This includes user input validation, data sanitization, and secure API communication with the backend.
Verdict
Laravel offers built-in security features for backend applications, making it a good choice for handling sensitive data and user authentication. React requires additional tools and best practices to achieve the same level of security.
Templating Engine
Laravel features the Blade templating engine, allowing developers to write clean, readable, and reusable templates. Blade templates are compiled into plain PHP and cached for better performance. It also supports template inheritance and sections, making it easy to manage complex views and layouts.
React, on the contrary, uses JSX (JavaScript XML), a syntax extension that allows developers to write HTML-like code within JavaScript. JSX improves the readability of the code and provides a seamless way to create and manage UI components. React’s component-based architecture promotes reusability and modularity, making it easy to build and maintain complex UIs.
Verdict
Both Blade and JSX are powerful templating systems in their respective domains. Blade is ideal for backend templating in Laravel, while JSX excels in creating dynamic and interactive UIs in React.
Built-in Tools
Laravel includes a rich set of built-in tools that streamline development. The Artisan CLI provides commands for tasks such as database migrations, seeding, and testing. Laravel’s built-in tools for task scheduling and event broadcasting simplify common development tasks. Plus, Laravel includes testing tools with PHPUnit and Dusk for browser automation.
React itself is lightweight and relies on the surrounding ecosystem for additional tools. The Create React App CLI helps create new projects with a pre-configured development environment. React’s ecosystem includes tools like Webpack for module bundling, Babel for JavaScript transpiling, and Jest for testing.
Verdict
Laravel’s built-in tools make the development process efficient for projects requiring common features. However, React’s integration with third-party libraries provides more flexibility for choosing suitable tools for specific needs.
Scalability
Laravel is well-suited for projects that start small and need to grow over time. Its structure allows developers to add more features to the existing code. With features like caching, database optimization, and load balancing support, Laravel can handle large and complex applications.
React is also highly scalable. Since it is component-based, you can reuse parts of the code across the project. This makes scaling easier and keeps applications efficient even as they grow. Combined with a strong backend, React can power very large applications used by millions of users.
Verdict
Both Laravel and React scale well, but in different ways. Laravel helps with backend growth while React ensures the frontend remains smooth and efficient as projects expand.
Learning Curve
Laravel is more manageable for beginners who know PHP. Its clear syntax, built-in tools, and documentation make it friendly to start with. However, mastering advanced features like queues, broadcasting, and complex database management can take extra time.
React can be trickier at the start. Concepts like JSX, state, and props may confuse beginners. But once you understand the basics, building UIs becomes much easier and faster. Its learning curve flattens over time with practice.
Verdict
Laravel is easier for those with a PHP background, while React requires a little more effort at the start but pays off in flexibility and speed later.
Community & Ecosystem
Laravel has a strong and active community. You will find plenty of tutorials, forums, and ready-to-use packages. Its ecosystem is stable and prosperous, with tools that make development easier.
React’s community is even larger and more global. It has a vast ecosystem of third-party libraries and frameworks built around it. From state management to testing tools, there are endless options available.
Verdict
Both have excellent communities. Laravel offers a more structured ecosystem, while React’s ecosystem is broader and gives more freedom to developers.
Deployment & Hosting Options
Laravel requires a server that supports PHP, typically in conjunction with MySQL or PostgreSQL. Many hosting providers support Laravel, but not all budget hosting plans are suitable. Deployment may require some setup knowledge, especially for scaling.
React, being frontend only, can be hosted almost anywhere. From free platforms like Netlify or Vercel to traditional cloud hosting, deployment is fast and straightforward. However, for full apps, React still needs a backend, which adds another step to deployment.
Verdict
React is easier and cheaper to deploy as a frontend library. Laravel requires more setup, but it provides full backend capabilities in one place.
Cost & Maintenance
Laravel projects may require more server resources, which can raise hosting costs. However, since many features come built in, you save time on development. Maintenance is straightforward if the code is well structured.
React is lightweight and cheaper to host. But because it depends on many third-party libraries, maintenance can be more challenging. You should keep updating packages to avoid issues.
Verdict
Laravel can be slightly more costly on hosting, but easier to maintain in the long run. React saves on hosting, but it requires more attention to keep libraries up to date.
Use Cases
Laravel is best suited for full-stack web applications that require both frontend and backend components in a single environment. Many eCommerce platforms, booking systems, and content-driven sites use Laravel because of its strong database handling and built-in security. For example, platforms like Koel and OctoberCMS are powered by Laravel.
React is ideal for building dynamic user interfaces. It is widely used in single-page applications, dashboards, and real-time apps. Large companies such as Facebook, Instagram, and Airbnb rely on React to deliver fast and interactive experiences to millions of users. React also works well when paired with a backend like Laravel or Node.js.
Verdict
Laravel is a strong choice for projects that need a secure backend and smooth database integration. React is the right pick for projects that require high interactivity and a seamless user experience at scale.
Explore This In-Depth Guide Next:
Final Verdict
Laravel and React are not necessarily competitors but rather complementary tools. Laravel excels in backend development, and React shines in building dynamic and responsive user interfaces.
The best choice depends on your project’s requirements. If you need a comprehensive framework for building a complex web application, Laravel is a great option. If your focus is on creating a dynamic and interactive user interface, React might be a better fit.
For full-fledged applications with a modern front-end, consider using Laravel and React together.
Conclusion
Laravel and React are complementary tools that can be used together to create powerful web applications. Here’s a quick recap to help you decide which technology is best suited for your project:
Choose Laravel if:
- You need a complete website with a robust backend and features like user management and security.
- You prioritize rapid development with the benefit of built-in tools and a simple templating engine.
- Your project focuses on content-heavy websites, and you want to leverage Laravel’s caching capabilities.
Choose React if:
- You’re building a Single Page Application (SPA) that requires a highly responsive and interactive user interface.
- You value flexibility in choosing UI libraries and tools based on your project requirements.
- Your project prioritizes a clean separation of concerns between frontend (React) and backend (Laravel) development.
This combination offers the best of both worlds: a secure and scalable backend with a user-friendly and responsive frontend. To leverage the power of both, you can hire web developers with us to build beautiful and robust sites.
FAQs About Laravel vs React
Can Laravel and React be used together?
Yes, Laravel and React can be used together to create powerful and efficient web applications. Laravel provides a backend structure and API, while React handles the frontend user interface.
Which one is better for scalability, Laravel or React?
Both Laravel and React are highly scalable and can handle large and complex projects. However, React’s component-based architecture makes scaling and maintaining code easier in the long run.
Do I need to know PHP to use React with Laravel?
Yes, a basic understanding of PHP is required to use React with Laravel, as Laravel is written in PHP. However, React itself does not require any knowledge of PHP as it is a JavaScript library.
Can Laravel and React be used together in a web project?
Yes, Laravel and React work very well together. Laravel handles the backend tasks like routing, database management, and security. React manages the frontend, creating a smooth and interactive user experience. Many modern projects use this combination to get the best of both worlds.
Which is better for scalability: Laravel or React?
Both are scalable, but they serve different roles. Laravel is great for scaling backend systems with features like caching, queues, and database optimization. React scales on the frontend by reusing components and efficiently handling UI updates. Together, they provide a scalable solution for large applications.
Do I need to know PHP to use React with Laravel?
You don’t need to know PHP to use React itself. React is purely a JavaScript library for the frontend. However, if you are integrating React with Laravel, having some PHP knowledge will help you understand the backend side better and work more smoothly with APIs.
Compare the best tech side by side.
Our in-depth comparisons help you see features, pros & cons, and choose the right tools confidently.





