Quick Summary
- PHP handles the logic and interaction of a web app, while SQL manages the data behind it. They have two different roles working together in one system.
- PHP runs the workflows users see, and SQL keeps the information structured, secure, and ready when the app needs it.
- Performance depends on improving each layer. PHP works better with caching and clean code. SQL relies on indexing and good queries.
- Real-world applications include eCommerce stores and SaaS dashboards. They rely on both PHP and SQL. This makes them a strong and useful pair for any modern web project.
Table of Contents
Any website that does real-time actions and stores information has two layers. One layer is the logic that runs the features. The other layer is the system that organizes the data. When people compare PHP vs SQL, they’re trying to understand how these layers work together and where each one plays its role.
PHP handles the dynamic side of a site. It runs the logic, builds the pages, and responds to user actions. SQL manages the data for those pages, storing, retrieving, and organizing the information a site needs to function. They work together in most database-driven applications, yet each solves a different problem.
In this blog, we will compare PHP and SQL. We will discuss their differences, how each technology works, and why they often coexist in web development. Let’s begin.
PHP: Quick Overview
PHP is one of the best server-side scripting languages, and it is used to build dynamic and interactive web applications. It controls how a website behaves, handles user actions, and prepares content before it reaches the browser. Developers use PHP to connect forms, pages, and features with real data. Its primary purpose is to bring logic and responsiveness to a site, making it work beyond static HTML.
PHP began in 1995 as a small toolset created by Rasmus Lerdorf to track visits on his personal website. Over time, it evolved into a full scripting language with strong community support. Regular updates have made PHP a stable and mature option for large-scale web projects.
Modern versions, including the latest PHP 8.4.8, released on June 5, 2025, offer better speed, stronger security, and cleaner syntax, keeping it highly relevant for today’s web development.
Key Features of PHP
- Server-side scripting: Runs on the server and generates the final output sent to the user.
- Integration with HTML: Works seamlessly with HTML, making page creation simple and intuitive.
- Support for frameworks (Laravel, CodeIgniter): Provides structured methods to build secure and organized applications.
- Session and form handling: Easily manages logins, forms, and user sessions.
Real-World Use Cases
- WordPress development: Powers the entire WordPress ecosystem and its plugins.
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, Magento): Manages carts, checkout flows, and product management.
- APIs: Helps build REST APIs for mobile apps and web platforms.
- Custom Web Apps: Used for dashboards, portals, booking systems, and more.
PHP Code Example
A small snippet that prints a simple message:
<?php
echo "Hello from WPWeb Infotech!";
?>
Put simply, PHP is used to build dynamic, interactive websites by handling user actions and managing content. It has evolved into a stable, secure, and fast language, with modern versions like PHP 8.4.8 supporting frameworks, session handling, and a wide range of real-world applications, including WordPress, eCommerce, APIs, and custom web apps.
If you’re planning to build or scale a PHP-based project, then you should hire PHP developers who can help you create high-performing applications faster and more efficiently.
SQL: Quick Overview
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is the standard language for managing and working with data in relational databases. It lets developers store, retrieve, update, and organize information in a structured way. SQL is used in almost all database-driven applications, from websites to business software.
Types of SQL Databases
Several relational databases use SQL, often with slight variations in syntax:
- MySQL: Widely used for web applications, known for speed and reliability.
- PostgreSQL: A Powerful, open-source database with advanced features and strong data integrity.
- MariaDB: A MySQL fork offering improved performance and community-driven development.
- SQL Server: Microsoft’s enterprise-level solution, often used in corporate and banking environments.
Key Features of SQL
- Data management: Organizes and stores data in structured tables for easy access.
- CRUD operations: Enables creating, reading, updating, and deleting records efficiently.
- Transactions: Ensures data integrity during multi-step operations.
- Schema design: Defines relationships, constraints, and structure of data to maintain consistency.
Real-World Use Cases
SQL is used to manage the databases behind many applications:
- Web app databases: Stores user accounts, content, and activity logs.
- Banking systems: Tracks accounts, transactions, and balances securely.
- SaaS products: Maintains client data, usage metrics, and subscription info.
- CRM & ERP systems: Handles customer records, sales, inventory, and reporting.
SQL Query Example
A simple query to fetch all users from a table:
SELECT * FROM users;
In short, SQL is the standard language for storing, retrieving, and managing data in relational databases. It is used across many applications, including websites and web apps, banking systems, SaaS products, and business software.
PHP vs SQL: Key Differences
Comparing PHP vs SQL side by side makes it easier to understand how each one fits into a project.
| Aspect | PHP | SQL |
|---|---|---|
| Platforms Support | Works on all major servers and operating systems | Works across many database systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, SQL Server |
| Audience | Developers who build web applications and backend logic | Developers and analysts who work with data and databases |
| Language Type | Server-side scripting language | Query language for relational databases |
| Purpose | Creates dynamic pages, handles requests, and controls app logic | Stores, retrieves, and manages data in structured tables |
| Execution Environment | Runs on a web server like Apache or Nginx | Runs inside a database engine |
| Output | Full caching support (Redis, Produces HTML, JSON, API responses, or other server output | Produces data results, tables, and records |
| Syntax Style | Similar to C-style syntax with functions and control flow | Simple, declarative commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE |
| Support | Large community, active updates, stable ecosystem | Broad support across many database vendors and tools |
| API | Works with APIs to handle requests and responses | Accessed through drivers or connectors from other languages |
| Free Verison | Fully free and open-source | Accessed through drivers or connectors from other languages |
PHP vs SQL: Performance & Scalability Differences
When you compare PHP and SQL from a performance angle, it’s helpful to remember that they solve different parts of a system. PHP handles the request, runs the logic, and prepares the response. SQL works within the database and handles storing and retrieving data. As a result, their speed and scalability depend on very different factors.
PHP Performance
PHP’s speed depends on how well the code is written and on how the server is configured. Modern versions of PHP, especially PHP 8+, run much faster than older releases thanks to improved engines and better memory handling.
PHP performs well when the logic is light, files are cached, and the application avoids unnecessary work. Most slowdowns happen when PHP makes too many database calls or handles heavy loops.
SQL Performance
SQL performance depends on the database engine, indexing, and query structure. Well-designed tables and proper indexing can return results in milliseconds. Poor schema design or unoptimized queries can slow down even the most powerful servers. SQL engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server handle large datasets and complex operations, but they still need clean queries to run efficiently.
Scalability
PHP can handle more users when you give it a stronger server, enable caching, or distribute the workload across several machines. Tools such as OPcache, CDNs, and load balancers help PHP run faster and reduce server load.
SQL grows in a different way. Because all the data is stored in the database, it can become the slowest part if not managed well. Databases improve performance by using indexes, cleaner queries, and copying data across multiple servers. Systems like PostgreSQL and SQL Server can handle large amounts of data, but they require proper planning as data and traffic grow.
In short, PHP’s speed depends on how the code runs on the server, while SQL’s speed depends on how well the database is structured and queried. PHP scales with better servers and caching, and SQL scales with indexing and smarter data management.
How PHP and SQL Work Together?
PHP and SQL both play different roles, but they depend on each other to transfer data between the user and the server. PHP handles the application’s logic, while SQL manages the data stored in the database.
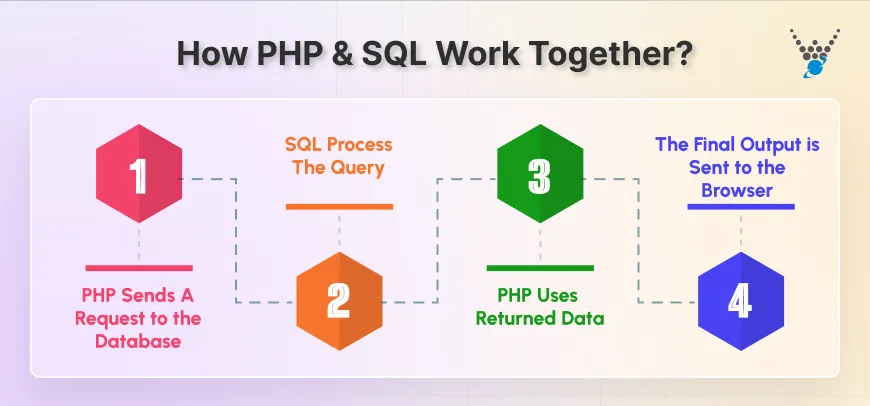
PHP Sends a Request to the Database
When a user clicks a button, submits a form, or loads a page that needs data, PHP steps in first. It reads the request, prepares an SQL query, and sends it to the database. It can be a request to fetch a user profile, check login details, or load product listings.
SQL Processes the Query
The SQL engine receives the query from PHP and searches the database for the required information. It reads the tables, checks indexes, applies filters, and returns only the data that matches the query.
The result could be a single row, a full list, or even a confirmation that new data has been added.
PHP Uses the Returned Data
After SQL returns the result, PHP interprets it and decides what to display on the page. It might display a list of items, show an error message, or update the user dashboard. It converts raw data into something meaningful for the user.
The Final Output is Sent to the Browser
PHP prepares the final HTML response with the updated information and sends it to the user’s browser. This cycle happens in milliseconds, which is why websites feel smooth and interactive.
PHP understands user actions such as clicks, forms, filters, and logins. SQL understands data, including storage, structure, and relationships. Together, they make dynamic websites work without confusion.
Below is an example workflow to help you better understand.
1. User clicks Login.
2. PHP receives the email and password.
3. PHP sends an SQL query to check the account.
4. SQL returns the matching record.
5. PHP shows the dashboard or an error message.
In short, PHP handles the logic of a web app, while SQL manages the data stored in the database. They work together by letting PHP send queries, SQL return the results, and PHP turn that data into the final output the user sees.
Connecting PHP to a MySQL Database
Connecting PHP to a MySQL database is one of the most common tasks in web development. It allows your PHP code to read, write, and manage data stored in the database. Without this connection, dynamic websites and applications cannot function properly.
Using MySQLi Extension
PHP offers the MySQLi (MySQL Improved) extension for connecting to MySQL databases. It is fast, secure, and supports both procedural and object-oriented programming.
Steps to Connect:
1. Define Database Credentials: Host, username, password, and database name.
2. Create Connection: Use the mysqli_connect() function.
3. Check Connection: Always verify if the connection was successful to avoid errors.
Example (Procedural):
<?php
$host = "localhost";
$user = "root";
$password = "";
$database = "my_database";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($host, $user, $password, $database);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
echo "Connected successfully";
?>
Using PDO (PHP Data Objects)
PDO is another method for connecting PHP to MySQL. It offers more flexibility and supports multiple database types, making it ideal for scalable applications.
Example:
<?php
try {
$pdo = new PDO("mysql:host=localhost;dbname=my_database", "root", "");
$pdo->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
echo "Connected successfully";
} catch(PDOException $e) {
echo "Connection failed: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
Below are some best practices that you should follow:
- Always handle errors: Use proper error handling to avoid exposing sensitive information.
- Use secure credentials: Avoid using default usernames and passwords in production.
- Close the connection: Free up resources after queries are executed.
- Consider PDO for scalability: PDO is better when you might switch databases in the future.
Connecting PHP to a MySQL database is the foundation for creating dynamic, data-driven websites. Once the connection is established, PHP can seamlessly retrieve, update, and display information, making your web applications interactive and user-friendly.
PHP vs SQL: Which One Should You Choose?
When deciding between PHP and SQL, it’s essential to understand that they serve different purposes, not as alternatives. PHP handles the application’s logic, user interactions, and dynamic content, while SQL manages and organizes the data behind the scenes. Choosing one over the other isn’t a question of preference but of understanding the role each plays in your project.
When to Focus on PHP
Choose PHP when your priority is building the functionality of a website or application:
- Creating interactive pages and forms.
- Handling user actions like login, registration, or searches.
- Connecting with APIs or third-party services.
- Developing content management systems, dashboards, or custom web apps.
PHP is essential for running the site’s logic. Without it, your website cannot respond to users or generate dynamic content.
When to Focus on SQL
Choose SQL when your main concern is managing and retrieving data efficiently:
- Storing and organizing large amounts of structured data.
- Performing queries to fetch, update, or delete records.
- Building reports or analytics from stored information.
- Managing applications that require high data integrity, like banking, CRM, or ERP systems.
SQL is vital for applications that rely on data storage and fast retrieval. Without it, the information your users input would have nowhere to go.
When to Use Both Together
In most modern web applications, PHP and SQL are used together:
- PHP handles user requests and application logic.
- SQL stores, retrieves, and organizes the data that PHP needs.
For example, an e-commerce site uses PHP to process a checkout form, while SQL stores the order, customer info, and inventory updates. Both are essential, and understanding how they interact will help you build efficient, reliable applications.
Simply put, PHP is the “action” layer, SQL is the “data” layer. Knowing when and how to use each ensures your web applications run smoothly, remain scalable, and provide a better experience for users. If you’re looking to build or scale applications with PHP and SQL, you should partner with a trusted PHP development company.
Explore our other programming language comparison blogs:
Closing Lines
Understanding the difference between PHP and SQL is essential for anyone building or managing a web application. PHP handles the logic, user interactions, and dynamic content, while SQL manages and organizes the data behind the scenes. Both work together to create responsive, data-driven websites and applications.
- PHP is for application logic, dynamic pages, and user interaction.
- SQL is used to store, retrieve, and organize data efficiently.
- Modern applications rely on both: PHP sends queries and SQL returns results.
- Performance and scalability depend on optimizing each layer: PHP through caching and server setup, SQL through indexing and query design.
- Knowing how PHP and SQL interact helps you build secure, efficient, and scalable web solutions.
In short, PHP and SQL are not alternatives, they complement each other. Knowing both gives you the control to create web applications that are fast, reliable, and easy to manage. Have a project in mind? Contact us to discuss PHP and SQL solutions tailored to your needs.
FAQs on PHP vs SQL
Is PHP better than SQL?
PHP and SQL serve different purposes, so one isn’t better than the other. PHP handles the logic, user interactions, and dynamic content of a website. SQL manages and retrieves the data stored in a database. Both are essential for building modern, database-driven applications, and they work best together.
Is PHP still worth it in 2025?
Yes, PHP is still worth learning and using in 2025. Modern versions, like PHP 8.4.8, offer faster performance, improved security, and better memory management. It remains widely used for web development, powering sites like WordPress, eCommerce platforms, and custom web apps. Its large community and extensive frameworks make it reliable for today’s projects.
Do companies still use PHP or SQL?
PHP is popular for building websites and web applications, with companies like Facebook (Meta), WordPress, Wikipedia, and Slack using it. SQL is used to store and manage data, trusted by companies such as Google, Amazon, Netflix, and Uber. Both are reliable, widely used, and essential in modern software development.
Consult PHP and SQL specialists
Consult PHP and SQL specialists to build secure, high-performance web applications.





