Quick Summary
Discover how to create a custom package for Laravel and unlock modular, reusable code for your projects. Learn step-by-step Laravel package development, from setting up service providers and facades to integrating configs, views, routes, and commands. Explore testing, publishing, and real-world examples to see how custom Laravel services and integration & customization can transform your applications into maintainable, powerful systems.
Table of Contents
Packages in Laravel websites help you design a unique user interface (UI) and craft exceptional features. There are several Laravel packages available for user management, email sending, image sending, and much more.
But what if you want some custom functionalities on your website? How to create a Laravel package tailored to your project? Well, our experts follow a step-by-step process to ensure the best results. Let’s take a look.
What Is a Package in Laravel?
In Laravel, a package is a reusable code module that adds specific functionality to your application. It is like a pre-built tool that processes a particular task, saving you time and effort compared to building from scratch. They are installed using Composer, making it easy to add and manage packages in your project.
A basic Laravel package development can include elements such as routes, controllers, views, configuration files, and even migrations. This shows the power and flexibility of using packages to extend Laravel’s functionality and build robust Laravel applications you can modify and call your own.
Why Create a Custom Package for Laravel?
While Laravel offers a rich set of features, there are situations where you need specific functionality for your project. This is where a custom package for Laravel comes in. By building your own, you can customize Laravel applications and integrate features that align with your exact needs.
Benefits of Creating Custom Package

- Code Reusability: Custom packages allow you to encapsulate and reuse code across multiple projects. This reduces the duplication effort and promotes a more efficient development process.
- Modularity: Packages help you break down your application into smaller, more manageable modules, making it easier to maintain and update, especially when using custom Laravel services.
- Flexibility: Custom packages can be built for your specific requirements, offering you control over the functionality and design of your application.
- Simplifies Maintenance: Packages isolate functionality, making it easy to locate and fix bugs without affecting other parts of your application.
- Ecosystem Integration: They can be integrated with the Laravel ecosystem, such as using Laravel’s service container, enhancing the functionality of your application.
If an efficient development process is followed, the above benefits can ensure a smoother user experience. To enhance your application’s performance by making it modular, hire Laravel developers to create custom Laravel packages.
Core Components in Custom Package for Laravel
1. Service Providers
Every custom package needs a Service Provider. It connects your package with Laravel’s core. Its role is simple but vital. It registers services, binds classes, and makes sure your package is available when the app boots.
Service Providers use two key methods: register() for binding your package’s services and boot() for loading everything when the application runs. The creation steps are straightforward: run php artisan make:provider to generate the file, then register it inside config/app.php. Once it’s in place, your package can cleanly talk to Laravel’s container.
This structure keeps your package organized and your code easy to maintain. You can say it’s the backbone of your integration.
2. Facades
Facades offer a simple interface to access your services without digging through layers of code. Their role is to give a clean, easy-to-use syntax that feels native to Laravel.
The creation process involves extending Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade and implementing the getFacadeAccessor() method. This method returns the container key your facade points to. Once built, alias the Facade in config/app.php, and it becomes instantly accessible throughout the app.
With facades, you make your package approachable. A single line can call a complex service behind the scenes.
3. Config Files
Config files give users the power to control how your package behaves. Their role is to allow easy customization without digging into the core code.
To set it up, create a PHP file inside the config directory. Developers can then access values using the config() helper function anywhere in their app. To make it flexible, publish your config file so users can override defaults. Then, merge the config in your Service Provider to keep everything in sync.
This small step gives your package a professional edge. It respects user preferences and keeps your code clean, stable, and easy to extend. If you’re looking to streamline admin panel development, Laravel Nova is a premium admin dashboard built to simplify backend management in Laravel applications.
How Can I Create a Custom Package for Laravel?
As we have seen the benefits of creating custom packages, let’s explore how you can create custom packages for Laravel applications. Here’s a step-by-step approach to start with:
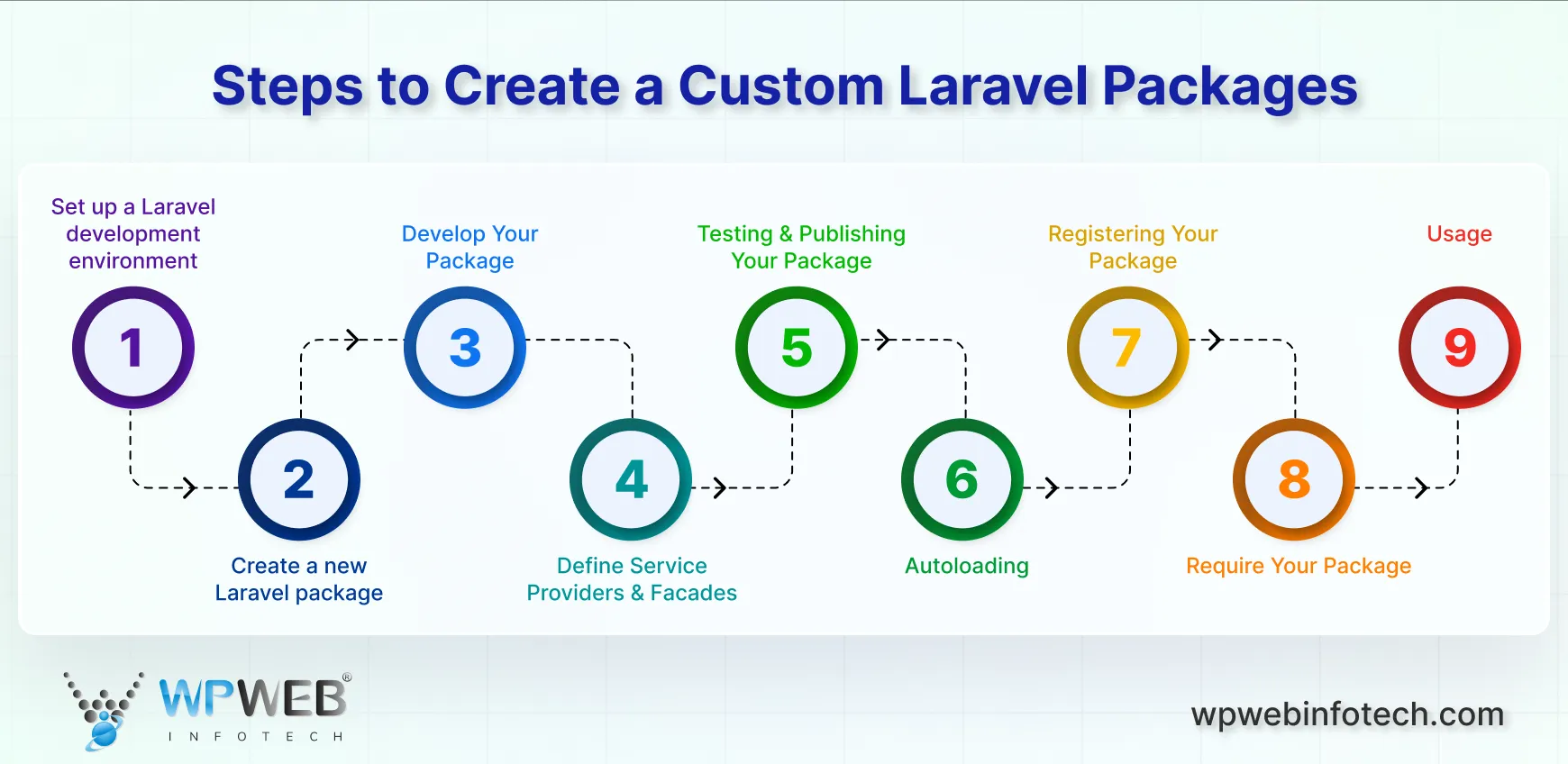
Prerequisites for Building Laravel Packages
Before crafting custom Laravel packages, ensure a smooth development process with these essentials:
- Solid Laravel Foundation: Grasp concepts like controllers in Laravel and Laravel Eloquent for building Laravel applications.
- PHP Proficiency: Possess intermediate PHP skills like syntax, OOP and familiarity with Laravel ecosystem helper functions.
- Composer Knowledge: Understand how to use Composer to install, manage, and update packages.
Step 1: Set up a Laravel development environment
Make sure you have Laravel installed on your machine. You can install it via Composer using the following command if you haven’t already:
composer global require laravel/installer
Step 2: Create a new Laravel package
Laravel provides a convenient tool called “Artisan” to help you create packages. Use Artisan to create a new package skeleton:
php artisan package:make YourVendorName/YourPackageName
Replace YourVendorName with your vendor name (e.g., your GitHub username or your company name), and YourPackageName with the name of your package.
Step 3: Develop Your Package
The previous command will create a new directory in the packages directory of your Laravel application. This directory will contain the basic structure for your package. You can start developing your package within this directory.
Step 4: Define Service Providers and Facades (Optional)
If your package needs to register service providers or facades, you can define them in the appropriate files (ServiceProvider.php and Facade.php). Do so within the src directory of your package.
Step 5: Testing and Publishing
Before releasing your package, ensure it is stable and production-ready. Exploring the top Laravel CMS platforms offers valuable insight into how modular concepts are applied to build flexible, scalable content management systems.
- Testing Environment Setup: Test your package in a fresh Laravel project to ensure everything works smoothly. This isolates issues and gives you a clean environment to debug.
- Publishing to Users: Once it passes testing, push your package to a version control platform like GitHub. This makes it accessible and easy to maintain.
- Distribution: Tag a release version and make it installable via Composer. A clear versioning strategy helps users trust and adopt your package easily.
Step 6: Autoloading
Make sure to autoload your package’s classes by adding the package’s namespace to the composer.json file of your Laravel application:
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"YourVendorName\\YourPackageName\\": "packages/your-vendor-name/your-package-name/src"
}
}
Step 7: Registering Your Package:
Register your package with Composer by adding a repository entry in the composer.json file of your Laravel application. Replace package-repo-url with the URL of your package repository:
"repositories": [
{
"type": "vcs",
"url": "package-repo-url"
}
]
Step 8: Require Your Package
For a real-world example of package-driven eCommerce, explore Bagisto Laravel – an open-source Laravel eCommerce platform built with modular architecture and reusable packages. Finally, require your package using Composer:
composer require yourvendorname/yourpackagename
Step 9: Usage
You can now use your custom package within your Laravel application by importing its classes or using its functionality as needed.
If you have followed us through, you may have a basic Laravel package that can help you explore more.
Integrating Resources (The SP’s Role)
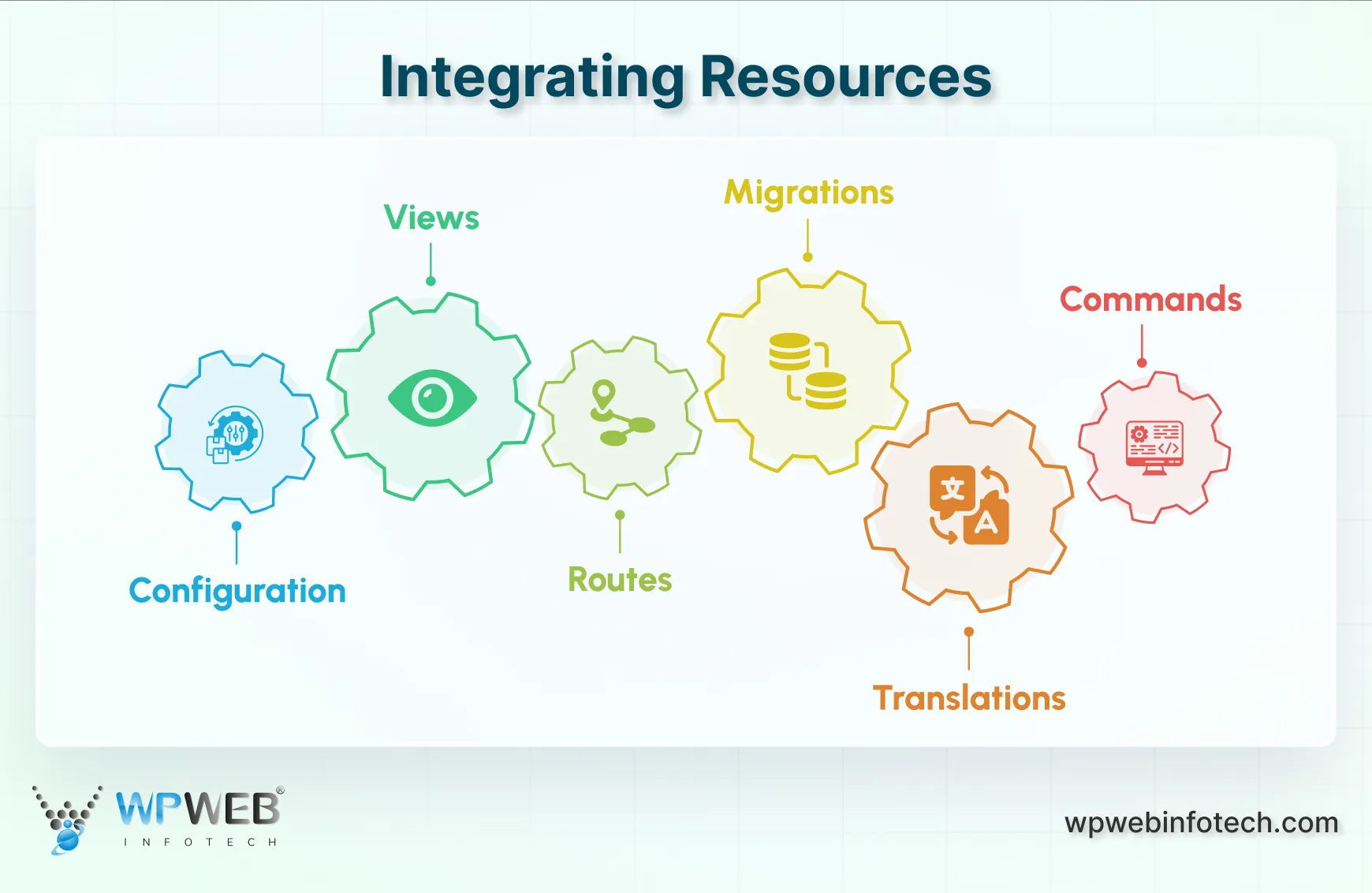
A Service Provider (SP) ensures all your resources, like configurations, views, routes, migrations, translations, and commands, are properly loaded and available. Let’s break down how each type of resource integrates through the SP.
1. Configuration
In the register() method, use mergeConfigFrom() to combine your package’s config with the application’s existing settings. This ensures defaults are available while still letting users override values.
In the boot() method, use publishes() to allow users to copy your config to their own config directory.
2. Views
Load your package’s views with loadViewsFrom() in boot(). For example, loadViewsFrom(__DIR__.’/../resources/views’, ‘package-name’).
To let users customize the views, publish them to resources/views/vendor/package. This creates a clean separation between your package defaults and the user’s overrides.
3. Routes
Include package routes using loadRoutesFrom() in boot(). This makes your routes automatically available without the user having to modify their web.php or api.php files.
4. Migrations
Call loadMigrationsFrom() in the boot() method to automatically register your package’s migrations. Users can then run php artisan migrate without manually copying migration files.
5. Translations
Use loadTranslationsFrom() in boot() to load your package’s language files. This lets your package support localization while keeping translations organized under resources/lang/vendor/package.
6. Commands
Register package commands with $this->commands() in boot(). This makes your console commands accessible via Artisan, giving users a seamless CLI experience.
This setup ensures your package integrates naturally into any Laravel application. To manage CRUD operations and admin tasks efficiently, consider using backpack for Laravel – a flexible admin panel tool that pairs perfectly with custom Laravel packages.
Conclusion
Creating a custom package for Laravel can enhance your development workflow by organizing and reusing code more efficiently. These packages offer seamless integration with your other Laravel projects. So you can create a modular and maintainable code base.
With proper documentation and testing, you can even consider publishing your package for the Laravel community on platforms like Packagist. Before publishing any package you create, ensure it is tested and follows best practices to contribute to the Laravel ecosystem.
If you are looking to create such packages, consider connecting with the Laravel development company to get the best results.
FAQs on Creating Custom Packages for Laravel
Can I update my custom package for Laravel after it has been published?
Yes, you can update your custom Laravel package after publication. Simply make the necessary changes to your package files and update the version number in the composer.json file. Then, publish the updated package using Composer.
How do I use a custom package in a Laravel project?
To use a custom package in a Laravel project, you need to add the package to the composer.json file of your Laravel project. You can then use Composer to install the package and use its functionality in your Laravel project.
How can I ensure my custom package is secure?
To ensure the security of your custom package, follow best practices such as validating user inputs, escaping outputs, and using Laravel’s built-in security features.
Let’s Build Your Custom Laravel Package
Need a tailored Laravel solution? Our experts can create custom packages that enhance functionality, boost performance, and perfectly match your project requirements.





