Quick Summary
Are you comparing Java vs C++ to choose the best programming language for your project? This blog discusses everything you need to know to compare them, from performance and memory control to use cases and emerging trends. Learn how Java powers cloud apps, AI, and enterprise systems, while C++ dominates gaming, IoT, and high-performance computing. Find out which language truly fits your project goals.
Table of Contents
The choice of programming language is a significant decision. And it depends on what you want to do with it. Comparing Java vs C++ is common, as both are popular options. Both languages are well-trusted and used in many software systems. But they take different approaches to how things get built and how fast they run.
Java is easier to learn, but C++ is better for speed and control. By understanding the actual difference between Java and C++, you can make a smart choice. So, in this blog, we’ll do a detailed C++ vs Java comparison based on their use cases, performance, learning curve, and more, so you can decide which is better for you. Let’s begin.
What is Java?
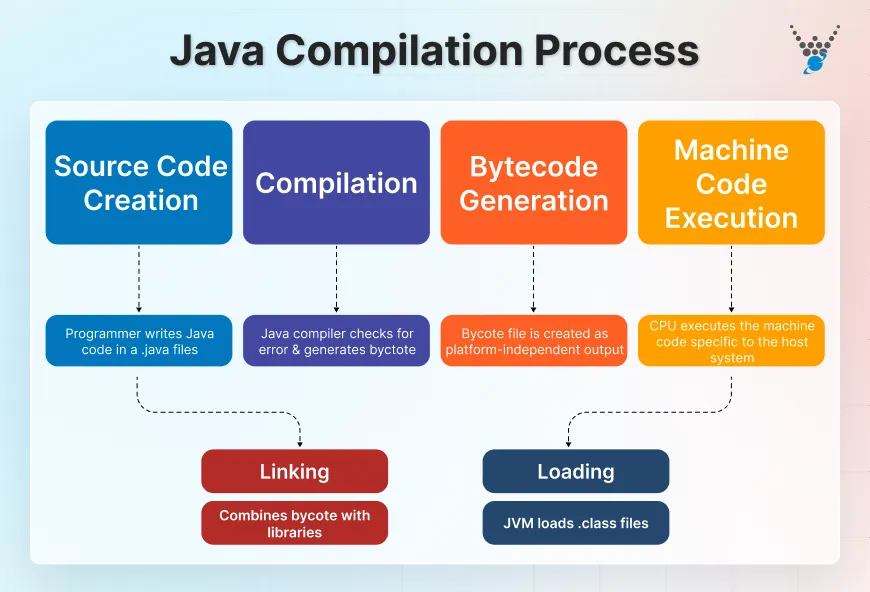
Java is an object-oriented programming language released in 1995. People know it for its “write once, run anywhere” nature. It doesn’t depend on the machine you use, which makes it a favorite for cross-platform software.
You’ll find Java in everyday laptops, Android apps, modern websites, and even large data systems behind major companies. It has helped create popular platforms like LinkedIn, Android, and Uber. It also helps with space technology, like the Mars Rover Controller.
Example:
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Hello WPWeb");
}
}
Output:
Hello WPWeb
Key Characteristics of Java
- Secure: Java takes security seriously. It restricts direct memory access and checks code before execution. It also has strong built-in security tools.
- Portable: Java programs can run on different systems without changes. Its architecture-neutral design makes moving software across devices easy.
- Robust: Java reduces common coding mistakes with strict compile-time checks and runtime monitoring. This keeps applications stable and reliable.
- Multithreaded: Java can handle many tasks at once, allowing developers to build interactive applications.
- Interpreted: Java translates bytecode into machine instructions at runtime. This supports faster development and easier debugging during the build process.
Use Cases
The common use cases of Java include:
- eCommerce portal development
- Application server management
- Android app development
- Enterprise software development
- Scientific computing application development
- Wearable tech design
Advantages and Limitations
The advantages of Java include:
- Large community: There are millions of developers contributing to libraries, tools, and quick solutions to common problems.
- Vast library: Java has many built-in features. These features make networking, database access, and UI development easy.
- Excellent tools: Integrated Development Environments like IntelliJ and Eclipse boost productivity with smart debugging and refactoring.
- Memory management: Garbage collection helps prevent memory leaks and reduces manual cleanup.
- Ecosystem: Popular Java frameworks like Spring make Java perfect for large, secure, and scalable business applications.
Limitations of Java include:
- Higher memory usage: Java applications often require more RAM than languages like C++ or Go.
- Slower startup time: The JVM needs to load and optimize code, which can delay execution for small or quick programs.
- Less control over hardware: Developers can’t easily manage system-level resources because of Java’s abstraction layer.
- Verbose syntax: Writing code in Java can feel lengthy and repetitive compared to newer languages.
Simply put, Java is an object-oriented programming language known for its WORA nature. It has a big community and a vast library with excellent tools. IDEs like IntelliJ and Eclipse boost productivity. If you want to build strong and scalable applications, hire Java developers. They can deliver your project with clean, efficient, and reliable code.
What is C++?
C++ is often called “C with classes.” It was developed to add classes to C in 1985. It is a compiled, statically typed language that supports multiple programming styles, including object-oriented programming. It is used for building video games, desktop applications, and embedded systems because it offers great control and efficiency.
The compatibility allows you to use most C code in C++. It is used in projects that demand high performance and real-time processing.
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
cout << "Hello WPWeb";
return 0;
}
Output:
Hello WPWeb
Key Characteristics

- Execution speed: Programs written in C++ run exceptionally fast, making it perfect for tasks that require performance.
- Memory control: Developers can manage memory directly, giving freedom to optimize systems.
- Rich standard library: It includes powerful tools for data structures, algorithms, and file handling.
Use Cases
C++ can be used to develop:
- Operating systems
- Video games
- IoT devices
- Databases
- Web browsers
- AR/VR applications
Advantages and Limitations
C++ brings many advantages:
- Performance-rich: Delivers higher speeds that make it a perfect choice for game engines, simulations, and trading platforms.
- Support for programming styles: Procedural, object-oriented, and even functional patterns work well in C++.
- Reusable code: Helps build efficient, modular software.
- Resource control: Allows precise tuning of hardware usage for better performance.
The limitations of C++ include:
- Lack of security: It is not a safer choice than Java. Experts say there are weaknesses in the memory codes.
- No garbage collector: Developers need to find and remove unnecessary properties on their own.
- Use of pointers: Pointers in the C++ language are difficult to understand and use.
In short, developers compile C++, use its static typing, and support multiple programming styles. It offers great control and efficiency, so it’s perfect for developing video games, desktop applications, and embedded systems.
Before moving to the next step, take a look at the resourceful Reddit thread discussing Java and C++, where you might find the answer you need. A Reddit user started with a discussion with – “I’m stuck choosing between Java and C++ ” and you’ll find many users mentioning their valuable experience with the user.
I’m stuck choosing between Java and C++
byu/SwedishNeatBalls inlearnprogramming
Java vs C++: Key Differences
C++ and Java both can increase your project’s efficiency, productivity, and delivery. Below is a quick comparison table that lists C++ vs Java differences to help you make a better choice.
| Factors | Java | C++ |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Management | Automatic garbage collection handles memory for you. | Users manage memory manually, though smart pointers can help automate handling. |
| Input and Output | Uses System.in and System.out for reading and printing. | Uses cin and cout for standard input and output operations. |
| Portability | Highly portable because of JVM support on almost every platform. | Less portable; it depends on the OS and compiler used. |
| Operator Overloading | Very limited, most operators cannot be overloaded. | Supports operator overloading and custom operations. |
| Compatibility | Works wherever JVM is available. | Closely tied to OS and hardware, so compatibility varies. |
| Language Level | High-level programming language. | Considered low-level and closer to hardware. |
| Pointers | Pointers exist but are hidden, used mainly for references. | Full pointer support, including direct memory address manipulation. |
| Libraries & Ecosystem | Full pointer support, including direct memory address manipulation. | Depends heavily on external libraries; strong system-level support. |
| Platform Dependency | Platform-independent once converted to bytecode. | Platform-dependent and needs separate compilation for each system. |
| Type System | Strongly typed and purely object-oriented. | Supports both procedural and object-oriented programming. |
| Multiple Inheritance | Does not allow multiple inheritance through classes. | Allows multiple inheritance for complex structures. |
| Structures & Union | Not available because Java uses classes for everything. | Fully supported — structures and unions are native features. |
| Real-World Applications | Used in web apps, business Used in web apps, business systems, mobile devices (Android), and cloud services. | Used in game engines, OS development, database software, and performance-critical systems. |
| Performance | Slower startup due to JVM; performance is optimized during runtime. | Faster execution because of direct hardware-level compilation. |
C++ vs Java: Performance Comparison
When we discuss performance, both C++ and Java work in vastly different ways. Below is a detailed explanation of how they compare in speed, memory use, and overall efficiency to see which one will deliver better results for your projects.

Speed and Execution Efficiency
C++ is usually faster because it compiles straight to machine code and works close to the hardware. This gives it an edge in game engines, real-time systems, and anything that needs instant response.
The performance of Java is also good, but there is an extra layer between the code and the machine as it runs on a JVM. For longer runtimes, JIT optimizations help it improve performance. But if raw speed is your priority, C++ still outperforms Java.
Memory Usage and Optimization
Memory is one of the key differences between C++ and Java. C++ allows developers to decide exactly how memory should be used. This reduces unnecessary memory usage and boosts performance. Smart pointers support this control while reducing errors.
Java chooses safety over control by using automatic garbage collection. This makes coding easier, but it can use more memory and cause slight pauses when cleanup happens.
Startup Time and Runtime Performance
Java has a slower start because the JVM must load and prepare the code before it can be executed. Once running, it optimizes performance over time. C++ launches quickly and remains fast throughout, as it does not require a virtual machine. In high-frequency tasks where every millisecond matters, C++ execution speed is a major advantage.
Resource Control (Manual vs Automated)
C++ offers full control over CPU, memory, and system resources. Developers optimize applications where performance is needed, which improves efficiency. But it also demands careful handling to avoid mistakes.
Java handles the cleanup automatically, which reduces risk and makes development easier for large teams. However, this safety may cause some performance drops.
Put simply, C++ has faster execution and better memory control, making it ideal for performance-critical applications. Java focuses on ease and safety with automated memory management, offering good speed but slightly less control over system resources. For optimal performance and reliability, partner with our Java development company. We can help you create secure, high-performance solutions that grow with your business.
Role of Java and C++ in Emerging Tech Innovations
Java and C++ are growing with new technologies like AI, cloud, and IoT. Both languages keep improving to stay fast, smart, and reliable for building modern software and future innovations.
Emerging Trends in Java
Java is continuously evolving to match modern software demands. Below are the top trends in Java’s future:
- Cloud-Native Development and Microservices: Java is moving from traditional monoliths to microservices. These microservices scale faster and work better in cloud environments.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: New libraries like DJL and Deeplearning4j help Java create smart systems. These systems can do things like detect fraud and make smart recommendations.
- Serverless and Event-Driven Applications: Lightweight frameworks and optimized runtimes are making Java a perfect choice for serverless workloads on major cloud platforms.
- Automation and DevOps Tooling: Teams using Java are adopting automated delivery pipelines. These pipelines speed up deployments and lower production errors.
- Performance Upgrades with GraalVM and Modern JVMs: Tools like GraalVM improve startup speed and lower memory use. This makes Java more competitive in high-performance settings.
Emerging Trends in C++
For performance-critical software, C++ is still the preferred choice. These trends are driving its continued dominance:
- Game Development and Real-Time Graphics: New engines and GPU-focused libraries keep C++ at the core of immersive 3D experiences and AR/VR worlds.
- High-Performance Computing and Scientific Simulations: C++ is a top choice in fields like aerospace, physics, and weather modeling. These areas need speed and accuracy.
- Advances in Embedded and IoT Systems: Its hardware-level access makes C++ ideal for smart devices, robotics, and autonomous systems.
- Modern C++ Standards (C++20 / C++23): New language features improve code safety, reduce bugs, and make development faster without losing control.
- Systems Programming and Cybersecurity Tools: C++ is still the top choice for operating systems and network tools. Developers also use it for security-focused applications that need low-level control.
In short, Java is growing stronger in cloud apps, AI, and automation, making it great for modern, scalable systems. C++ stays unbeatable in gaming, IoT, and high-performance computing, thanks to its speed, precision, and control.
Additional Backend Comparison Guides:
Wrapping Up
Choosing between Java and C++ depends on what you want to build and how much control you need. To build large-scale business systems, cloud apps, or Android development, Java provides stability and a smooth learning path. It focuses on security and reliability, which companies require for long-term growth.
If performance is non-negotiable for you, C++ should be your pick. It offers deeper access to hardware, faster execution, and precise resource control. That makes it the right fit for games, real-time engines, and advanced computing systems. And if you’re not sure about which language you should choose, you can contact us for expert assistance!
FAQs on Java vs C++
Can Java match C++ in performance?
Java can perform like C++, but it usually runs a little slower. This is because it uses the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) instead of running directly on the hardware. But for most business and web applications, this difference is barely noticeable. With modern JVM optimizations, Java performs efficiently enough for most large-scale systems.
Which is better for web or enterprise apps – Java or C++?
Java is the better choice for web and enterprise apps. It offers strong security, scalability, and a wide range of frameworks like Spring and Hibernate. C++ is a powerful language. However, it is better for system-level or performance-heavy applications. It is not ideal for large, distributed web systems.
How does developer availability impact the total cost of ownership?
You can easily find Java developers as it is a widely used language. The no. of C++ developers is less, and they are often expensive to hire due to the language’s complexity. So, building and maintaining Java projects typically costs less over time.
Need Guidance on Java vs C++?
Need help choosing between Java and C++ for your next project? Our experts can guide you based on your goals, performance needs, and budget.





