Quick Summary
Master Laravel Horizon from setup to production in this guide. Learn how to monitor queues in real-time, balance workers automatically, handle failed jobs, and gain actionable metrics. Explore real-world use cases such as email campaigns, image processing, and large-scale data imports. Get expert tips on production setup, optimization, troubleshooting, and scaling across multiple servers to ensure reliable, high-performance background job management.
Table of Contents
Imagine a situation where your application suddenly needs to handle thousands of jobs at once. Emails, notifications, reports, all queued up and waiting. Without proper queue management and efficient task scheduling in Laravel, your app will slow down. Users will get frustrated, and critical tasks will pile up.
This is where Horizon in Laravel steps in. For developers aiming for professional-grade Laravel apps, mastering queues is essential. Laravel Horizon is known for its:
- Real-time monitoring: Track job status and failures instantly on a clean, intuitive dashboard.
- Advanced queue management: Handle multiple queues, prioritize jobs, and scale across servers effortlessly.
- Ease of setup: Configure supervisors, metrics, and alerts without complex hacks.
In this blog, we discuss the process of installing and configuring Laravel Horizon. This will help you manage multiple queues and prioritize jobs for better performance. You’ll be able to monitor and analyze job performance with Laravel Horizon metrics. So, let’s start from the basics.
What is Laravel Horizon?
Laravel Horizon is a tool that helps you manage and monitor your queue workers in Laravel. Think of it as a control panel for your background jobs. Instead of guessing what happens behind the scenes, Horizon shows you everything live – what’s running, what failed, and how your queues are performing.
But how is it different from standard Laravel Queues? In Laravel queues, you can run workers using simple commands, and they will process jobs. But the default setup gives you very little visibility. You can’t easily see job history, retry failures, or scale workers without manual effort.
Horizon changes that.
It adds:
- A visual dashboard to monitor all queues in real-time
- The ability to assign priorities, run multiple queues, and scale workers easily
- Automatic job performance tracking with detailed Laravel Horizon metrics
Here is a visual overview of Horizon architecture:
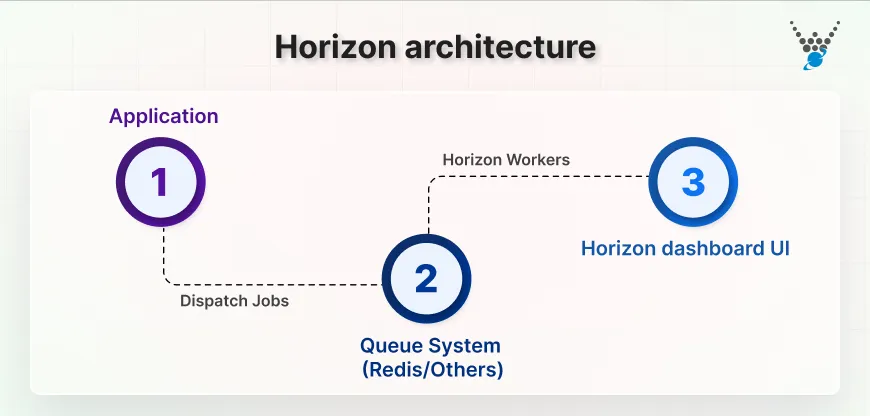
This shows how jobs move from your app → to the queue → processed by Horizon workers → monitored in the dashboard.
You should use Laravel Horizon when your app runs many background jobs and you need clear visibility into what’s happening. It’s ideal if you manage multiple queues, set priorities, or plan to scale across servers. If your app only sends a few emails, you may not need it. But once reliability and performance matter, Horizon becomes essential.
If you want to implement Laravel Horizon smoothly and ensure your queues are optimized for scale and reliability, hire Laravel developers who can set up, configure, and monitor your background jobs efficiently.
Core Features of Horizon
Before we install anything, it helps to understand what makes Horizon valuable in real projects. These core features are the reason teams rely on it when queues start growing and reliability becomes essential.
Real-Time Monitoring Dashboard
Horizon gives you a live, browser-based dashboard that displays pending, running, completed, and failed jobs. You can spot backlog spikes or a sudden failure pattern at a glance. That reduces guesswork and speeds up fixes.
For example, if your email queue jumps from 5 to 1,000 pending jobs after a campaign, you’ll see the surge and spin up extra workers.
Automatic Job Balancing
Horizon can automatically rebalance worker processes across queues using built-in strategies (auto, simple, false). The right balance keeps fast queues fast and prevents hotspots from starving other work. It reduces manual tuning when traffic changes.
For example, using the auto balance, Horizon increases the number of processes for notifications when its pending count and average wait time climb, then shrinks them when the peak passes. You can also set minProcesses and maxProcesses for safety.
Failed Job Management
Horizon logs failed jobs, shows the error and stack trace, and lets you retry or remove failures from the UI. This enables you to fix production issues faster because you see the cause and can requeue or drop failures without digging through Redis or raw logs.
Suppose a payment job fails due to a third-party timeout. Horizon will display the exception and payload so you can fix the job, then retry the failed batch from the dashboard.
Metrics and Insights
Horizon records metrics such as throughput, average runtime, wait time, and failure rates for each queue and worker. These metrics let you make data-driven decisions: when to add workers, which jobs to optimize, and where to set priorities.
Quick example: If Horizon shows email jobs’ runtime doubling during business hours, you can schedule extra worker capacity only during those peak windows to cut delivery time.
Simply put, Laravel Horizon provides real-time visibility, automatic workload balancing, tools for failure recovery, and performance metrics that help your queues stay stable as they grow. Instead of guessing what’s happening behind the scenes, Horizon lets you monitor, diagnose, and scale background jobs with clarity and control, making Laravel pipelines easier to manage.
How to Install and Configure Laravel Horizon
Before installing Laravel Horizon, make sure your setup meets these requirements:
- Composer installed: Horizon depends on Composer, the PHP dependency manager. Make sure it’s installed and accessible from your terminal.
- Running Laravel project: You need a Laravel application ready. Horizon works best on Laravel 5.7 or higher. If you don’t have a project yet, create one following Laravel’s official installation guide.
- Redis running: Horizon relies on Redis as the queue backend. Ensure Redis is installed and active on your local machine or server.
Queue connection configured: In your .env file, set QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis so Laravel knows to use Redis for background jobs.
Quick Setup
Here are the three essential steps.
Step 1: Installation
Run:
composer require laravel/horizon
Then publish Horizon’s assets:
php artisan horizon:install
This pulls in the package and sets up the basic files.
Step 2: Basic configuration
Open config/horizon.php and make only the essential adjustments:
- Ensure your environments array has entries for local and production (or your custom env).
- For now, leave defaults like balance => ‘auto’, queue => [‘default’], maxProcesses => 3 in local.
- Set the dashboard route access (via HorizonServiceProvider) so only your team or admin users can reach it.
Step 3: First run
Start Horizon with:
php artisan horizon
Expected output (sample):
Horizon started successfully.
Processing: 3 workers
Watching connection: redis - queues: default
Visit the dashboard (/horizon) and you’ll see live job counts, workers, etc. If the page loads and shows you data, you’re good to go.
To sum up, installing and configuring Laravel Horizon requires a Laravel project, Composer, and a running Redis instance, with QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis set in your .env. After installing via Composer, adjusting basic settings in config/horizon.php, and starting Horizon, you can immediately monitor and manage your queues from the dashboard.
Production-Ready Setup
Setting up Laravel Horizon for production is more than just running php artisan horizon. To ensure reliability, performance, and security, you need proper configuration, monitoring, and scaling. Here’s a focused, expert guide.
Supervisor Configuration
Supervisor keeps Horizon workers running in the background and restarts them if they fail. Let’s take a look at a working example for Ubuntu:
Create a supervisor config file: /etc/supervisor/conf.d/horizon.conf
[program:horizon]
process_name=%(program_name)s
command=php /path/to/your/project/artisan horizon
autostart=true
autorestart=true
user=www-data
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/path/to/your/project/storage/logs/horizon.log
stopwaitsecs=3600
Commands to enable and start:
sudo supervisorctl reread
sudo supervisorctl update
sudo supervisorctl start horizon
Without Supervisor, your workers stop when the terminal closes or the server restarts.
Environment Variables
Configure your .env for production carefully:
- QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis: ensures Horizon uses Redis.
- HORIZON_PREFIX=horizon_prod: isolates Horizon data if multiple environments share Redis.
- APP_ENV=production: enables production mode for logging and caching.
- APP_DEBUG=false: hides sensitive information from errors.
Proper environment variables prevent conflicts, accidental data leaks, and performance issues.
Security Considerations
- Dashboard access: Protect /horizon with authentication or IP restrictions.
- HTTPS: Always serve the Horizon dashboard over HTTPS to secure credentials and job data.
- Sensitive job data: Avoid storing secrets in job payloads or logs. Use encrypted storage if necessary.
Scaling Guidelines
- Multiple servers: Horizon supports running workers across multiple machines. Use Redis as a central queue to coordinate jobs.
- Multiple queues: Prioritize jobs by creating separate queues (high, default, low) and assigning dedicated workers.
- Worker count: Start with a conservative number of workers and monitor CPU/memory usage, then scale gradually.
In short, a production-ready Horizon setup requires Supervisor to keep workers running, properly configured environment variables, and strict security measures like dashboard authentication and HTTPS. Scaling involves multiple servers, prioritized queues, and careful monitoring of worker count and resource usage to ensure reliability and performance.
Real-World Use Cases
The following examples show how Horizon helps optimize workflows, reduce delays, and maintain system responsiveness while giving you full visibility into every job.
Email Queue Management
Sending thousands of newsletter emails in a single request can overload your server, slow down other processes, and risk emails landing in spam due to sudden bursts.
Horizon Configuration:
- Use a dedicated emails queue.
- Assign higher priority to transactional emails (high) and lower priority to newsletters (low).
- Configure 3-5 workers for emails queue with auto-balancing enabled.
- Set retry_after to a safe interval (e.g., 120 seconds) to avoid duplicate sends.
Results / Metrics:
- Email backlog reduced from 5,000 pending to zero in under 10 minutes.
- Transactional emails always processed first, maintaining user engagement.
- Dashboard metrics showed stable worker utilization with no spikes in failures.
Image Processing Pipeline
Generating multiple thumbnails for hundreds of uploaded images can consume CPU heavily and block other jobs if processed synchronously.
Horizon Configuration:
- Create a media queue dedicated to image jobs.
- Split processing into multiple smaller jobs per image (original, medium, thumbnail).
- Configure 4-6 workers with auto-balanced processes.
- Monitor throughput and adjust maxProcesses for peak upload hours.
Results / Metrics:
- Average image processing time dropped from 12 seconds per image to under 4 seconds per image.
- No blocking of other queues; user requests remained responsive.
- Metrics dashboard showed even worker load and minimal failed jobs.
Data Import Jobs
Large CSV imports can time out, fail partially, or lock the database, resulting in a poor experience for admins uploading bulk data.
Horizon Configuration:
- Use a data_import queue.
- Split the CSV into chunks (e.g., 500 rows per job) to prevent long-running jobs.
- Configure 2-3 workers with retry and failure tracking enabled.
- Use Horizon metrics to monitor job runtime and queue backlog in real-time.
Results / Metrics:
- 100,000-row CSV imported in under 15 minutes without database locks.
- Failed rows automatically logged; retries succeeded without manual intervention.
- Dashboard metrics enabled proactive scaling by increasing worker count during heavy import windows.
Simply put, Laravel Horizon streamlines real-world workflows by efficiently managing email queues, image processing, and large data imports, preventing bottlenecks and improving reliability. Proper queue configuration, worker scaling, and monitoring reduce backlog, speed up job processing, and maintain system responsiveness.
Monitoring & Optimization
To manage queues effectively, you need to continuously observe, measure, and tune performance. Laravel Horizon provides the tools, but knowing what to watch and how to act separates a reactive setup from a production-grade system.
Key Metrics to Watch
Monitor these metrics regularly to detect issues before they impact users:
- Pending Jobs: Watch for spikes above normal thresholds. Example: more than 50 pending jobs in default queue may indicate a bottleneck.
- Failed Jobs: Keep failures under 1-2% of total jobs. Any sudden rise signals an external dependency or coding issue.
- Average Runtime: Track runtime per job type; if a job consistently exceeds expected runtime (e.g., >5 seconds for emails), it may need optimization.
- Throughput: Jobs processed per minute; sharp drops may indicate worker issues or Redis saturation.
Performance Optimization Tips

- Queue Segmentation: Split job types into separate queues (e.g., high, default, low) to prevent critical jobs from being delayed by bulk processes.
- Worker Scaling: Adjust the number of workers dynamically using Horizon’s auto-balance feature to handle traffic spikes efficiently.
- Chunking Heavy Jobs: Break large tasks (CSV imports, image processing) into smaller jobs to reduce execution time and memory usage.
- Retry Strategy: Set appropriate retry_after and maximum attempts to prevent duplicate processing while ensuring jobs aren’t lost.
Alerting Setup
Proactive alerts help catch issues before they escalate:
- Email or Slack notifications for failed jobs or queue backlogs exceeding thresholds.
- Custom notifications for slow jobs that exceed the expected runtime.
- Integration with monitoring tools like Laravel Telescope, Grafana, or Prometheus for real-time alerts.
Dashboard Customization
Horizon’s dashboard can be tailored to focus on your key workflows:
- Filter by queue: Show high-priority queues first.
- Worker metrics: Highlight the most critical workers or servers.
- Job types: Use color-coding to spot job categories that are slow or failing.
- Time windows: Adjust charts to see trends over hours, days, or weeks.
With these monitoring and optimization practices, Horizon becomes more than a queue manager. It become a live performance observatory for your Laravel application, helping you catch bottlenecks early, optimize resource usage, and maintain a smooth user experience.
Common Issues to Troubleshoot
Even with a solid setup, queue systems can run into friction. The key is to recognize the symptoms quickly and apply the right fix. Below are the issues you’ll encounter most often, along with what causes them and how to resolve them.
Jobs Stuck in “Pending”
Cause: Workers are not running or Horizon is not actively supervising queues.
Solution: Restart Horizon and ensure Supervisor is managing the process.
php artisan horizon:terminate
sudo supervisorctl restart all
If you’re running locally:
php artisan horizon
Memory Exhaustion
Cause: A job consumes more memory than workers are allowed, causing silent worker restarts.
Solution: Increase memory limits and chunk large workloads.
In config/horizon.php:
'defaults' => [
'supervisor' => [
'maxProcesses' => 5,
'memory' => 256, // MB
],
],
For heavy loops, process in batches:
Model::chunk(500, function ($records) {
// process each batch
});
Supervisor Not Restarting Horizon
Cause: The Supervisor config does not auto-reload, or the autorestart option is missing.
Solution: Update Supervisor config:
[program:horizon]
command=php /var/www/html/artisan horizon
autostart=true
autorestart=true
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/horizon.log
Then reload:
sudo supervisorctl reread
sudo supervisorctl update
sudo supervisorctl restart horizon
Redis Connection Issues
Cause: Incorrect Redis host or Redis is not running.
Solution: Verify Redis status:
redis-cli ping
Check .env:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis
REDIS_HOST=127.0.0.1
REDIS_PORT=6379
If using Docker, host may be redis instead of 127.0.0.1.
Slow Job Processing
Cause: Queue congestion or not enough workers handling high-volume queues.
Solution: Allocate more workers to high-traffic queues:
In config/horizon.php:
'production' => [
'supervisor-high' => [
'connection' => 'redis',
'queue' => ['high'],
'balance' => 'auto',
'maxProcesses' => 10,
'minProcesses' => 3,
],
],
Then:
php artisan horizon:terminate
Horizon will restart and rebalance automatically.
To put it briefly, common Horizon issues include jobs stuck in pending, memory exhaustion, Supervisor not restarting, Redis connection problems, and slow processing. Most problems can be resolved by restarting Horizon, adjusting worker memory and count, verifying Redis, and ensuring Supervisor is correctly configured.
Horizon vs. Alternatives
Horizon occupies a specific niche: it serves as a visibility and control layer built specifically for Laravel. To understand its strengths, it helps to compare it with running queues without Horizon and with other queue ecosystems.

| Feature | Ease of Use | Features & Control | Performance Profile | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laravel Horizon | Very easy if you’re in Laravel. Native integration and a guided dashboard. | Real-time monitoring, auto balancing, metrics, failed job UI. Purpose-built for Redis queues. | Fast and stable for most Laravel workloads. Scales horizontally across multiple workers/servers with ease. | Free. Only Redis/server costs. |
| Laravel Queues | Simple to start but hard to manage at scale. Requires manual CLI checks and logging. | No dashboard. Limited visibility. Troubleshooting requires digging through logs. | Performs fine, but harder to optimize since you lack metrics and queue insights. | Free. But higher maintenance cost. |
| Sidekiq | Polished and mature, but Ruby ecosystem required. Not plug-and-play for PHP. | Excellent dashboard, scheduling, and job pipelines. Rich ecosystem. | High-performance and proven at very large scale. | Open-source version free. Pro features licensed. |
| Bull | Good for teams already working in Node. Developer-friendly API. | Basic UI via 3rd-party add-ons. Horizontal scaling needs tuning. | Fast for lightweight tasks. Can hit performance ceilings under very heavy queues. | Free. Costs mainly in ops complexity. |
Best Practices Checklist
Even the most well-configured Laravel queue system can run into hiccups, so it’s crucial to know the common issues and how to fix them quickly.
Configuration
Your configuration should make Horizon predictable and stable. Always set QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis across every environment so the queue behavior doesn’t change silently. Run Horizon under Supervisor or systemd to ensure workers restart when they exit or crash.
Separate your queues by priority rather than pushing everything into default; this prevents slow jobs from blocking urgent work. In horizon.php, define minProcesses and maxProcesses so Horizon knows how far it can scale without overwhelming the server. Finally, keep this configuration in version control to avoid accidental drift between staging and production.
Performance
Focus on keeping your job light and focused. Avoid sending large data blobs inside job payloads; write them to storage or a database and pass only references. If a task is heavy, like video encoding or PDF generation, move it to a dedicated queue so it doesn’t slow down others.
Watch queue wait time rather than just job count; rising wait times indicate you’re falling behind. When jobs frequently write to the database, use batch operations to reduce contention. And as workloads grow, run Redis on its own machine or container so it doesn’t compete with PHP workers for CPU and memory.
Security
The Horizon dashboard should never be publicly reachable. Wrap it in authentication middleware and allow access only to operational or admin roles. Also, make sure Redis itself is secured, bind it to localhost or a private network, and enable authentication when supported.
Treat queue monitoring access the same way you’d treat database admin access: controlled, logged, and limited.
Monitoring
Good monitoring prevents silent backlog and invisible failures. Track wait time and runtime trends over days, not just snapshots; they reveal stress patterns as load changes. Configure alerts when pending jobs exceed a safe threshold for a sustained period, rather than reacting only when something breaks.
Make it a habit to review failure logs regularly because recurring failures are rarely random. They usually indicate missing retry logic or an unreliable external dependency. Effective monitoring helps you fix issues before customers notice them.
Conclusion
Laravel Horizon makes queue management easy and clear. By providing real-time monitoring, automatic job balancing, insights into failed jobs, and rich performance metrics, it ensures your queues run smoothly, reliably, and efficiently.
You should consider implementing Horizon when your application handles high-volume jobs, needs prioritized queues, or must maintain reliability across multiple servers. If you find yourself manually checking queues, chasing failed jobs, or dealing with unpredictable job processing, Horizon is the tool that solves these problems systematically.
Need help implementing Horizon in production? Partner with a Laravel development company that can guide you through setup, configuration, and scaling so your Laravel queues stay robust, visible, and high-performing.
FAQs on Laravel Horizon
Can Horizon handle millions of jobs?
Yes. Horizon is built on Redis, which is fast and memory-efficient. With proper worker scaling and queue segmentation, it can process millions of jobs reliably without blocking other tasks.
What’s the performance overhead?
Minimal. Horizon adds monitoring and metrics on top of standard Laravel queues. The main overhead comes from dashboard updates, but workers themselves run at nearly native queue speed.
Do I need Redis?
Yes. Horizon is designed specifically for Redis queues. Without Redis, it won’t function, as Redis handles job storage, state, and fast queue operations.
Can I use multiple servers?
Absolutely. Horizon supports multiple servers processing the same queues. Redis coordinates jobs across all workers, ensuring jobs aren’t duplicated and workloads stay balanced.
How much does it cost to run?
Horizon itself is free. Your main costs come from infrastructure: Redis server(s), PHP workers, and any cloud resources needed for scaling high-volume queues.
Master Laravel Horizon Fast
Learn how to set up and monitor Laravel Horizon with real examples and tips from experts.





