Quick Summary
Laravel performance depends heavily on how efficiently your application interacts with the database. This guide explores essential optimization techniques, from eager loading and indexing to caching, batching inserts, and schema design, to reduce query load and boost scalability. You’ll also learn how to monitor performance using Laravel Debugbar, ensuring fast, reliable, and high-performing applications as your data grows.
Table of Contents
Optimizing Laravel database queries is crucial for making your application run faster and smoother. Slow queries can lead to poor performance and a bad user experience. That’s why experts prioritize query optimization as a key step in improving the speed and responsiveness of web apps.
In this blog, we’ll cover easy-to-follow tips and best practices to help you optimize Laravel database queries. Whether it’s using eager loading, caching, or optimizing indexes, these methods will help make your app more efficient. Let’s get started!
Why Optimize Database Queries?
Your application’s performance depends on its database. Ignoring query efficiency creates tangible problems. Optimizing your Laravel database queries solves them. Below is what changes:
- Faster Application Response: Slow queries create lag. They force users to wait for simple actions. Optimized queries eliminate this friction. The result is a swift, immediate feel that keeps users engaged. This is the core of Laravel performance optimization.
- Reduced Server Load: Bad queries waste resources. They demand excessive CPU cycles and memory. This unnecessary strain can cripple your server during traffic spikes. Effective Laravel query optimization reverses this. It frees up server capacity, often reducing infrastructure costs.
- Better Scalability: This refers to your application’s ability to grow and expand. Poor queries will cause failure as your user base expands. A well-optimized system, built with smart database query optimization techniques, remains stable. It prepares your application to handle increased demand without costly rewrites.
In short, optimizing your Laravel database queries provides a faster user experience and a more stable, cost-effective foundation for your application.
How to Optimize Laravel Database Queries?
It is essential to optimize database queries if you want to improve the performance of your Laravel application. Here are some tips to help you optimize Laravel database queries:
1. Use Eloquent ORM Efficiently:
- Eloquent is Laravel’s integrated ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) system. It offers a convenient way to work with database tables and streamlines database interactions.
- Utilize eager loading, lazy loading, and Eloquent relationships to reduce the number of queries and boost performance.
Example:
//Eager loading example
$posts = Post::with('comments')->get();
2. Choose the Right Database Indexes:
- You can significantly speed up query execution by properly indexing your database tables.
- Analyze your queries, add indexes manually to columns that are frequently used in WHERE clauses and JOIN operations, or use Laravel migrations that use the ->index() method.
Example:
// Migration with index
Schema::create('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->index('email'); // Index on the 'email' column
$table->timestamps();
});
3. Limit the Number of Columns Selected:
- Avoid using SELECT when requesting data from the database. Only select the columns you need.
- Reduce the amount of information that is transferred between the database server and the application.
Example:
// Select specific columns
$users = DB::table('users')->select('name', 'email')->get();
4. Pagination Large Result Sets:
- Use the built-in pagination in Laravel to restrict the number of records fetched per query when fetching large result sets.
- In addition to ensuring quicker page loads, this also prevents memory problems.
Example:
// Paginate query results
$posts = Post::paginate(10);
5. Caching:
- Use caching for frequently used queries or data that does not change often.
- The caching system offered by Laravel supports a number of cache stores, including Redis, Memcached, and file-based caching.
Example:
// Caching query results for 10 minutes
$users = Cache::remember('users', 10, function () {
return DB::table('users')->get();
});
6. Database Queue Optimization:
- Utilize Laravel’s built-in queue system to offload time-consuming database operations.
- Due to the asynchronous processing of tasks, this can speed up response times for user-facing requests.
Example:
// Dispatch a job to a queue
dispatch(new ProcessOrder($order));
7. Avoid N+1 Query Problems:
- The N+1 query problem is a looping extra query that looks for related records.
- To fetch related records in a single query, use eager loading (with).
Example:
// Eager loading to avoid N+1 queries
$posts = Post::with('comments')->get();
8. Database Transactions:
- To ensure data consistency and prevent incomplete updates in the event of errors, use database transactions in Laravel when making multiple database changes.
Example:
// Using transactions
DB::transaction(function () {
// Your database operations
});
9. Database Query Logging:
- To identify slow or ineffective queries, enable query logging in your development environment.
- Reviewing executed queries is simple thanks to Laravel’s query log.
Example:
DB_LOG=true
10. Database Index Optimization:
- To find slow queries, periodically examine your database’s query execution plans.
- Use tools like Laravel Debugbar or database query profiling to find bottlenecks.
11. Database Design:
- Make sure your database design adheres to best practices, such as normalization and denormalization, depending on the demands of your application.
- Avert data duplication that is not necessary. For applications using Laravel multiple databases, query optimization becomes more complex. Each database connection may have different performance characteristics, and you need to ensure queries are optimized for each specific connection.
12. Consider Database Sharding or Replication:
- Consider database replication for read-heavy workloads or database sharding to distribute data across multiple servers for very high traffic applications.
- Your application can be horizontally scaled by putting these strategies into practice.
13. Use Appropriate Database Drivers:
- Pick the best database driver for your unique use case. Numerous database drivers, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, and others, are supported by Laravel.
Example:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
14. Regularly Update Laravel and Database software.
- For performance gains and security updates, keep your Laravel database and application software up to date.
15. Profiling and Benchmarking:
- To locate performance bottlenecks and areas that require optimization, use profiling and benchmarking tools.
- You can monitor application performance using tools like Laravel Telescope.
Database query optimization is a continuous process. Maintain regular performance monitoring of your application, and use profiling tools to pinpoint areas that could be made better. By adhering to these recommendations, you can make sure that your Laravel application functions well and scales successfully as your user base expands.
And if you don’t have the expertise to optimize the database, let a Laravel development company take care of it.
Best Practices to Optimize Laravel Database Queries
As your Laravel application becomes more complex and the volume of data increases, optimizing database queries is essential for maintaining high performance, reducing server load, and ensuring scalability. Laravel offers powerful tools and techniques to ensure that database operations run efficiently.
Here are the key best practices for achieving faster and more optimized database queries:
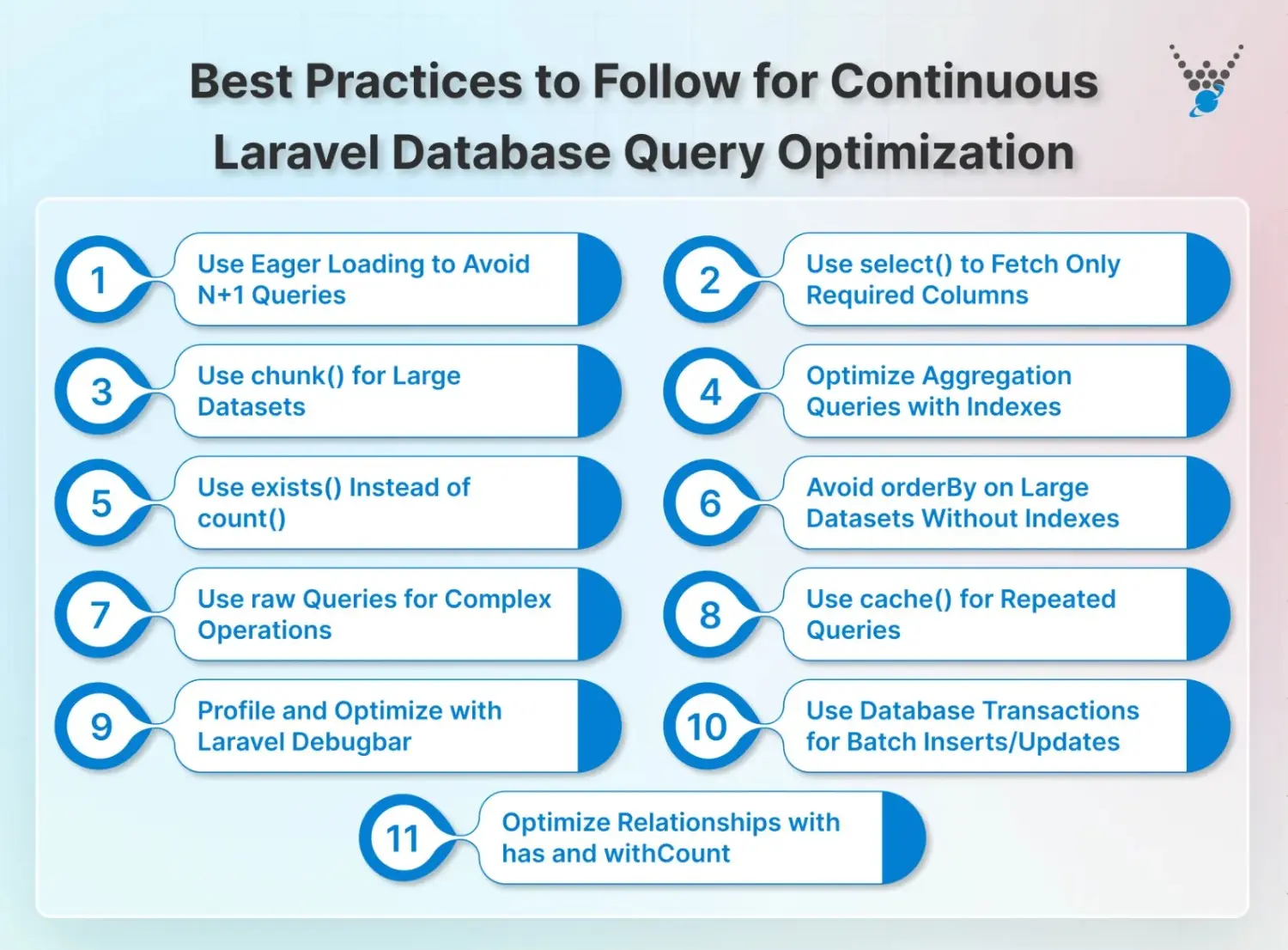
Efficient Data Retrieval
Use Eager Loading to Avoid N+1 Queries
The N+1 query issue occurs when a related model loads inside a loop — causing numerous unnecessary queries.
Inefficient
$posts = Post::all();
foreach ($posts as $post) {
foreach ($post->comments as $comment) {
//
}
}
Optimized
$posts = Post::with('comments')->get();
Tips
- Use with() to load relationships efficiently
- Chain multiple relations:
Post::with([‘comments’, ‘author’])->get();
Use Nested Eager Loading for Deep Relationships
When relationships go multiple levels deep (e.g., comments → user), use nested eager loading:
$posts = Post::with('comments.user')->get();
Use select() to Fetch Only Needed Columns
$users = User::select('id', 'name', 'email')->get();
Avoid retrieving unnecessary columns like large text or JSON fields.
Use pluck() for Single Column Retrieval
pluck() is faster when you only need one column:
$userEmails = User::pluck('email');
Handling Large Datasets
Use chunk() for Batch Processing
User::chunk(100, function ($users) {
foreach ($users as $user) {
//
}
});
Use chunkById() or cursor() for Better Memory Efficiency
Prevents issues when new records are inserted during processing:
User::chunkById(100, function ($users) {
//
});
Streaming approach using generators:
foreach (User::cursor() as $user) {
//
}
Query Optimization Techniques
(including tools like using Laravel Debugbar to monitor and analyze query performance)
Use exists() Instead of count()
if (User::where('email', $email)->exists()) {
//
}
Avoid orderBy on Unindexed Columns
Always index columns used in sorting:
Schema::table('posts', function ($table) {
$table->index('created_at');
});
Optimize Aggregation Queries with Proper Indexes
Indexes drastically improve performance for:
- count()
- sum()
- avg()
- groupBy()
Avoid Leading Wildcards in LIKE Searches
Avoid this:
WHERE name LIKE '%john'
Database cannot use indexes. Prefer:
WHERE name LIKE 'john%'
Avoid SQL Functions in WHERE Clauses
Avoid wrapping columns in functions, prevents index usage:
// Avoid
User::whereRaw('YEAR(created_at) = 2025');
// Better
User::whereBetween('created_at', [$start, $end]);
Merge Similar Queries to Reduce DB Hits
Use whereIn() or bulk data retrieval instead of looping multiple queries.
$users = User::whereIn('id', $ids)->get();
Skip belongsTo Relationship Load If Only ID Needed
Instead of:
$post->author->id;
Use:
$post->author_id;
Write Efficient Queries
Use Raw Queries for Complex Operations
DB::table('users')
->select(DB::raw('TIMESTAMPDIFF(YEAR, birth_date, CURDATE()) as age'))
->get();
Use sparingly → sanitize inputs.
Optimize Relationships with has() and withCount()
User::has('posts')->get();
User::withCount('posts')->get();
Efficiently Retrieve Latest Rows Using orderBy + Index
Post::orderBy('created_at', 'desc')->limit(10)->get();
Ensure indexed column.
Insert & Update Optimization
Use Database Transactions for Batch Operations
DB::transaction(function () {
DB::table('orders')->insert([...]);
});
Ensures consistency + reduces locking. This is especially helpful during large data imports such as database seeding in Laravel, where thousands of records may be inserted at once.
Use Bulk Inserts for Multiple Records
DB::table('users')->insert([
['name' => 'Adam'],
['name' => 'Bella']
]);
Avoid looping inserts.
Caching Queries
Use Cache for Repeated Queries
$users = Cache::remember('users', now()->addMinutes(10), fn () => User::all());
Invalidate Cache When Data Changes
Use cache tags when data is related:
Cache::tags(['users'])->flush();
Structuring Database Schema for Performance
Add Indexes on Frequently Queried Columns
Foreign keys, search filters, ordering fields, etc.
Avoid Too Many Columns in a Single Table
Normalization supports:
- faster reads
- smaller row size → more rows per page
Move Large Text / JSON Fields Into Separate Tables
For blog posts, separate structure:
posts (id, title, created_at)
post_contents (post_id, content TEXT)
Improves SELECT performance on high-traffic tables.
Simply put, Laravel query optimization ensures applications remain fast and scalable by improving how data is retrieved, processed, and stored. For in-depth query analysis, use Laravel Debugbar to monitor query count and execution time. Following best practices such as eager loading, indexing, caching, batching operations, and schema optimization significantly reduces query load and enhances overall performance.
Let’s Conclude
Optimizing database queries in Laravel is crucial for building fast and scalable applications. By implementing these techniques—like eager loading, caching, and using indexes—you can drastically reduce query times and improve your application’s performance.
Tools like Laravel Debugbar also make it easy to identify inefficiencies, making optimization a straightforward process. With these strategies, your Laravel application will be ready to handle more data and deliver a faster user experience.
If you need advanced customizations for your Laravel app or want assistance with performance optimization, hire expert Laravel developers.
FAQs
Can improving database queries speed up Laravel file uploads?
Yes, Metadata, user associations, and database file records are needed for Laravel file upload efficiency. Optimizing database queries with indexes, chunked inserts, and eager loading speeds up uploads, file lookups, and user experiences. This is crucial for websites with many file uploads or media records.
How does Laravel MySQL dump protect data during query optimization and app updates?
Performing a Laravel MySQL dump before optimizing queries or changing your application provides a snapshot of your current database. This backup is essential for data restoration following a migration, query error, or system update. Developers can securely test indexing, schema updates, and optimization methods with regular dumps.
Optimize Laravel Database Queries Like a Pro
Improve your Laravel app's performance by learning how to optimize database queries.





