Quick Summary
Discover how Laravel Passport simplifies secure API authentication, offering robust token-based protection for your applications. Learn key concepts such as clients, access tokens, grants, and scopes, and see step-by-step how to implement OAuth 2.0 in Laravel. Compare Passport with Sanctum to choose the right tool for your project. This guide makes complex API security simple, practical, and ready for real-world use.
Table of Contents
To build a modern web application, ensuring secure communication between the frontend and backend is a must. Users share private data every day, including emails, financial transactions, and personal information. They want it to remain safe. Laravel Passport API Authentication makes this possible.
It provides a clean way to set up secure API authentication without having to reinvent the wheel. Instead of going through tokens and complex setups, you can rely on a trusted package built right into the Laravel ecosystem.
In this blog, we’ll discuss what Passport is, why it matters, and how it works in practice. So, let’s dive in!
What is Laravel Passport?
Laravel Passport is an official Laravel package that acts as a full-fledged OAuth2 server implementation. In simpler terms, it provides a secure and standardized way to authenticate users for your Laravel application’s API.
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, are essentially the behind-the-scenes messengers. They allow different parts of your application (or even external applications) to communicate with each other.
Since APIs don’t rely on sessions (like traditional web applications do), Laravel Passport utilizes tokens to manage user access. This ensures that only authorized users can access specific functionalities or data within your Laravel app’s API.
It’s like a digital lock and key system with access only to those with the right credentials.
Key Concepts of Laravel Passport
Laravel Passport empowers you to secure your Laravel application’s API with the industry-standard OAuth2 protocol. But to leverage its full potential, you need to understand some key concepts.
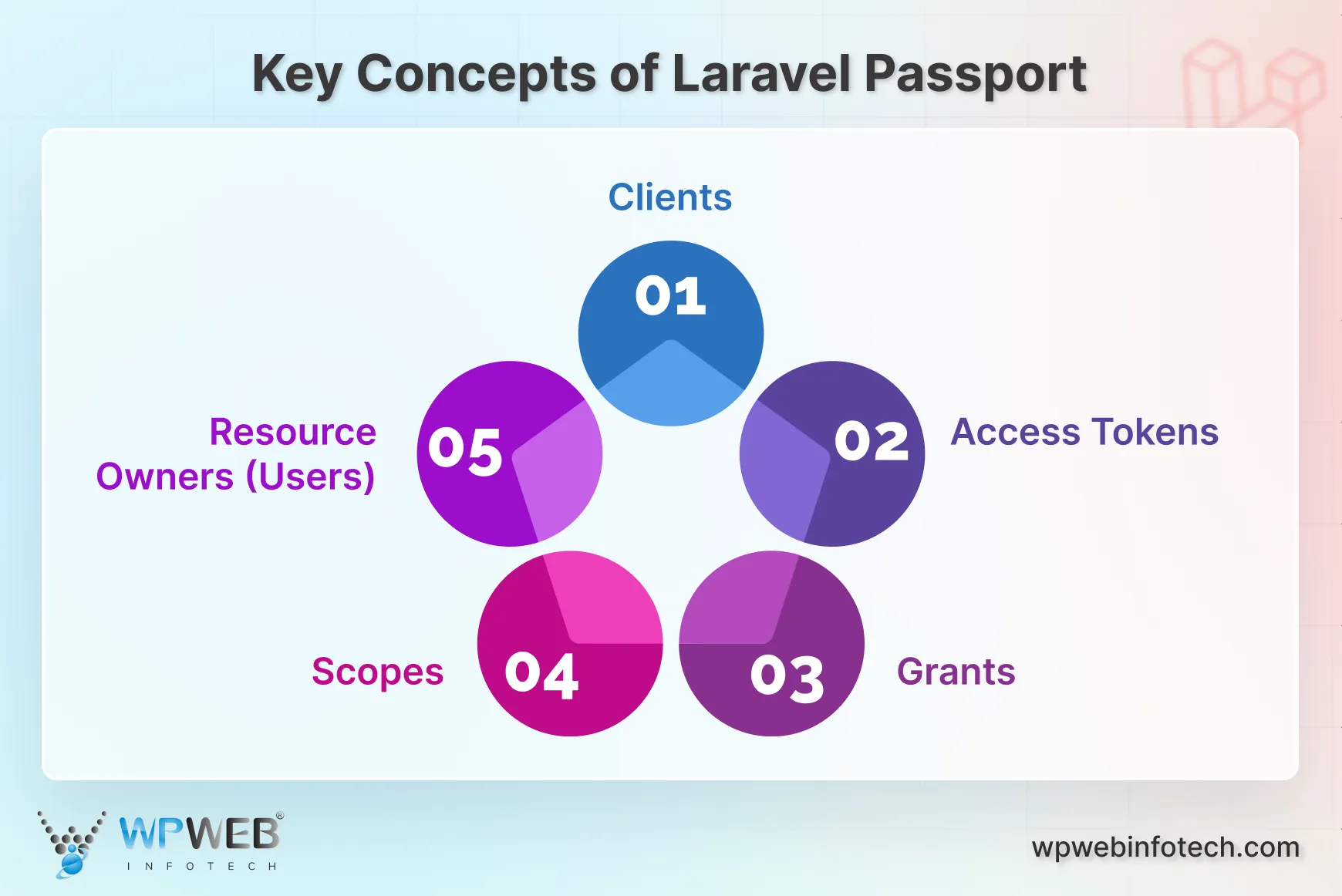
- Clients: These represent the applications or services that will be requesting access to your API. You’ll need to create client credentials (like a client ID and secret) within Laravel Passport to identify and authorize these clients.
- Access Tokens: These are essentially digital keys that grant access to your API’s resources. Once a client is successfully authenticated, Laravel Passport issues a time-bound access token. Subsequent API requests from the client must include this token for authorization.
- Grants: These define the different methods clients can use to obtain access tokens. Laravel Passport supports various grant types, including popular options like Password Grant (for user login) and Authorization Code Grant with PKCE (for improved security).
- Scopes: Scopes allow you to set granular access levels within your API. You can define specific functionalities or data sets that a particular access token grants access to. This enables you to create a more secure and controlled environment within your API.
- Resource Owners (Users): These are the individuals who will be accessing your API through authorized clients. In most cases, these will be the users of your Laravel application. Laravel Passport integrates seamlessly with Laravel’s user authentication system.
By mastering these concepts, you can implement robust and secure user access controls. That takes your Laravel project’s security to the next level.
Benefits of Laravel Passport
Laravel Passport offers a plethora of benefits that can significantly enhance your Laravel application’s security and functionality. Here’s a breakdown of some key advantages:
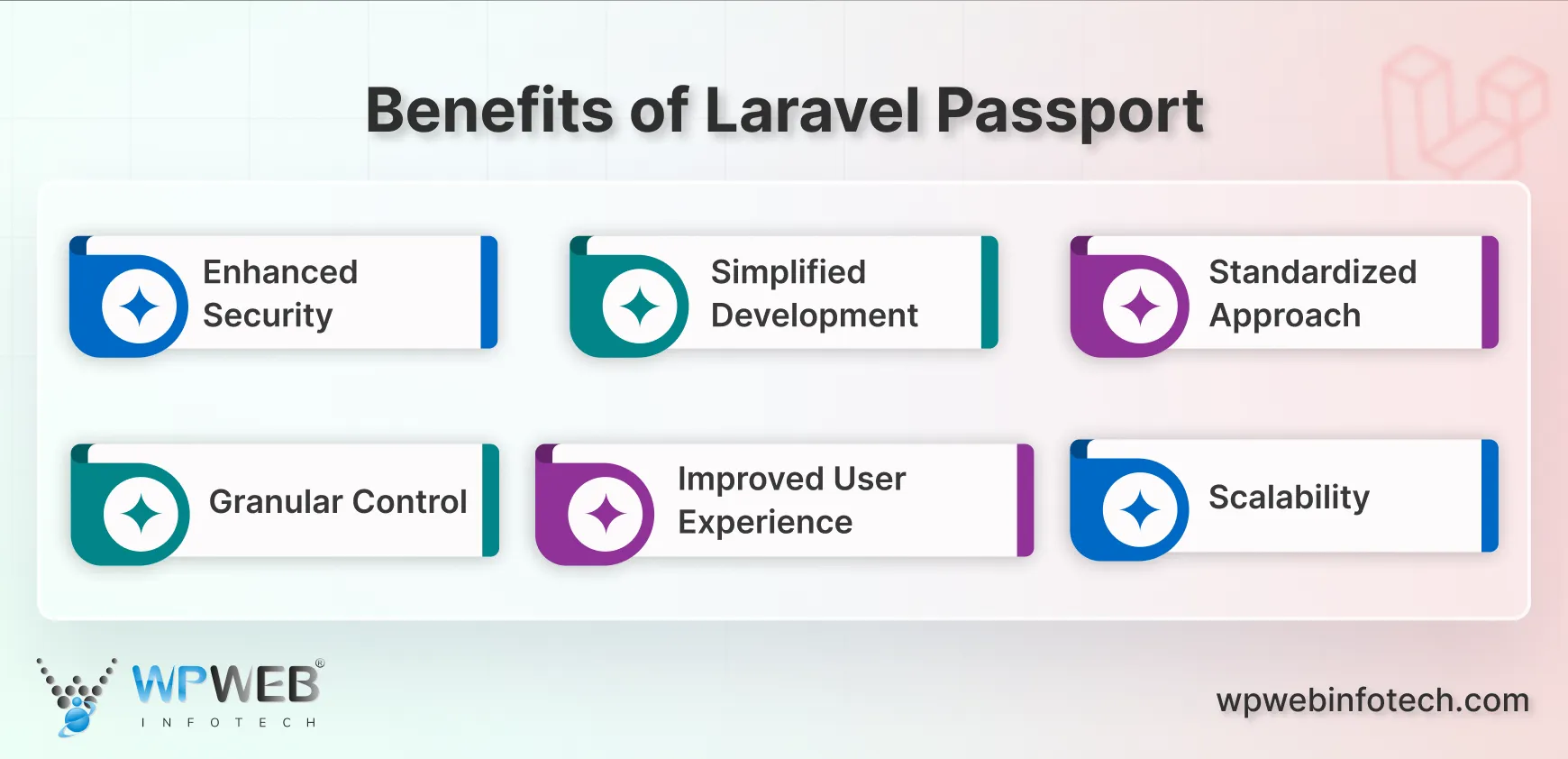
- Enhanced Security: By implementing OAuth2 authorization, Laravel Passport throws up a robust security shield around your application’s API. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data or functionalities, minimizing vulnerabilities and protecting your users’ information.
- Simplified Development: Integration of Laravel Passport is remarkably straightforward. The package offers a well-documented and easy-to-understand API, allowing you to quickly implement secure authentication without getting bogged down in complex coding.
- Standardized Approach: Laravel Passport leverages the industry-standard OAuth2 protocol. That ensures seamless integration with various third-party applications and services. This promotes compatibility and simplifies future development endeavors.
- Granular Control: With Laravel Passport, you have the power to define granular access levels for your API. This enables you to restrict access to specific functionalities or data sets based on user roles or permissions. That creates a more secure and controlled environment.
- Improved User Experience: Laravel Passport’s token-based authentication translates to a smoother user experience. Users won’t need to repeatedly log in for each API interaction, streamlining the overall user flow. You can connect user accounts securely with platforms like Google, Facebook, or Twitter using Laravel Socialite for social media.
- Scalability: As your Laravel application grows, Laravel Passport’s secure and scalable architecture can handle the increased demands. This ensures your API remains secure and reliable even with a larger user base.
By incorporating Laravel Passport into your Laravel project, you’ll gain a powerful tool for securing your API and streamlining user access. These benefits make it a valuable addition to the Laravel security toolkit. For additional methods of login, registration workflows, or securing both frontend and API routes, options within Laravel Authentication Systems.
Laravel Passport vs Laravel Sanctum: When to Use Which
When building APIs in Laravel, you have two main tools for authentication: Laravel Passport and Laravel Sanctum. Both are excellent, but they serve slightly different needs. Choosing the right one depends on your project’s requirements.
Passport in Laravel is designed for full OAuth2 authentication. It works well when you need secure token-based access for complex applications. This is ideal for APIs that will be used by third-party clients or mobile apps. Laravel Passport API Authentication handles access tokens, refresh tokens, scopes, and Laravel Passport Grant Types, making it perfect for applications that need fine-grained control over user access. Gain control over user roles, team permissions, and enterprise-level RBAC by using approaches from Advanced User Management in Laravel.
On the other hand, Laravel Sanctum is simpler. It works best for first-party applications, such as a Single Page Application (SPA) built with Vue or React that communicates with the same Laravel backend. Sanctum uses API tokens or cookie-based authentication, which is easier to set up and manage. It doesn’t require OAuth2 complexity, so it’s lighter and faster to implement.
How to decide:
- Use Passport in Laravel when you need robust security, multiple client access, or external third-party integrations.
- Use Sanctum when building internal APIs or SPAs where simplicity and speed are more important than full OAuth2 features.
Both tools are made by the Laravel team and integrate seamlessly with Laravel’s authentication system. Understanding their strengths helps you make informed choices and keeps your application both secure and efficient.
How to Use Laravel Passport for Authentication?
Laravel Passport provides a full OAuth2 server implementation for your Laravel application, enabling secure token-based authentication for your APIs. Here’s how you integrate it.
Step 1: Installation and Setup Laravel Passport
Begin by installing Passport via Composer in your Laravel project:
composer require laravel/passport
Next, run the migrations to create the tables Passport needs to store clients and access tokens:
php artisan migrate
Now, install Passport. This command will create the encryption keys needed to generate secure access tokens:
php artisan passport:install
Note the output of this command, specifically the Personal access client and Password grant client IDs and secrets, as they may be needed for frontend configuration.
Step 2: Configure Model and Service Provider
In your App\Models\User model, add the HasApiTokens trait:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Laravel\Passport\HasApiTokens; // <-- Add this
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
class User extends Authenticatable
{
use HasApiTokens, HasFactory, Notifiable; // <-- Use the trait
}
Then, within the boot method of your App\Providers\AuthServiceProvider, register the routes Passport uses to issue and revoke tokens:
use Laravel\Passport\Passport;
public function boot(): void
{
// ... other policies
Passport::tokensExpireIn(now()->addDays(15));
Passport::refreshTokensExpireIn(now()->addDays(30));
Passport::personalAccessTokensExpireIn(now()->addMonths(6));
}
Finally, in your config/auth.php configuration file, set the API driver to passport.
'guards' => [
'api' => [
'driver' => 'passport', // <-- Change from 'token' to 'passport'
'provider' => 'users',
],
],
Step 3: Define API Routes and Controllers
Create API routes in routes/api.php that use the auth:api middleware. This middleware will automatically validate incoming access tokens. Apply different authentication guards in API, web, or admin areas by leveraging strategies found on how to use the Auth Guard in Laravel.
Route::get('/user', function (Request $request) {
return $request->user();
})->middleware('auth:api');
Step 4: Obtaining an Access Token (Password Grant Example)
To authenticate a user and retrieve an access token, your frontend client (e.g., a Vue.js SPA or a mobile app) must make a POST request to your application’s /oauth/token endpoint.
curl -X POST http://your-app.com/oauth/token \
-H "Accept: application/json" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"grant_type": "password",
"client_id": "your-password-grant-client-id",
"client_secret": "your-password-grant-client-secret",
"username": "user@example.com",
"password": "password",
"scope": ""
}'
A successful response will return a JSON object containing an access_token and a refresh_token.
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 1296000,
"access_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI...",
"refresh_token": "def50200ae2d6d4d5a3c2a..."
}
Step 5: Make Authenticated API Requests
The frontend client must now include this access token in the Authorization header of every subsequent API request.
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI…
The auth:api middleware will validate this token and automatically load the associated user model. That makes it available via $request->user() in your route or controller.
While the Password Grant is common for first-party clients, Passport supports all OAuth2 grants. For a first-party JavaScript SPA, it’s recommended to use the Laravel Sanctum package instead.
If you want a more advanced authentication setup and more for your web app, get our expert Laravel development services. We can also help you with custom Laravel package development, if required for your project.
Let’s Conclude
Laravel Passport allows developers to easily add OAuth2 authentication to their applications. It provides a secure and standardized way for users to authenticate and access APIs. Using Laravel Passport can save developers time and effort in implementing authentication from scratch.
This package offers a convenient and secure way to implement OAuth2 authentication with minimal effort. It also integrates well with the Laravel framework, making it easy to use alongside other Laravel features such as middleware and routing.
If you want to implement this package or any other for your website or application, hire Laravel developers today!
FAQs on Laravel Passport
Can Laravel Passport be used for both server-to-server and user-to-server authentication?
Yes, Laravel Passport supports both server-to-server and user-to-server authentication. For server-to-server authentication, clients can use a private key to sign requests. For user-to-server authentication, users can authorize the client to access their resources.
Can I use Laravel Passport with non-Laravel applications?
Yes, Laravel Passport can be used with non-Laravel applications. It provides a set of API endpoints that can be used to authenticate and access APIs. However, some features may be specific to Laravel, so it may require some extra effort to integrate with non-Laravel applications.
Are there any limitations to the number of users or clients that can be authenticated with Laravel Passport?
There are no specific limitations to the number of users or clients that can be authenticated with Laravel Passport. However, the performance of your application may be affected if you have a large number of clients or users. It is recommended to use caching and other optimization techniques to ensure optimal performance.
Can Laravel Passport work with other Laravel starter kits like Jetstream?
Integrating Laravel Jetstream with Passport allows you to combine robust user management features and advanced authentication flows in the same application.
Implement Secure API Authentication Easily
Use Laravel Passport to protect your APIs with OAuth2. Our experts can help you set it up for seamless, secure integration.